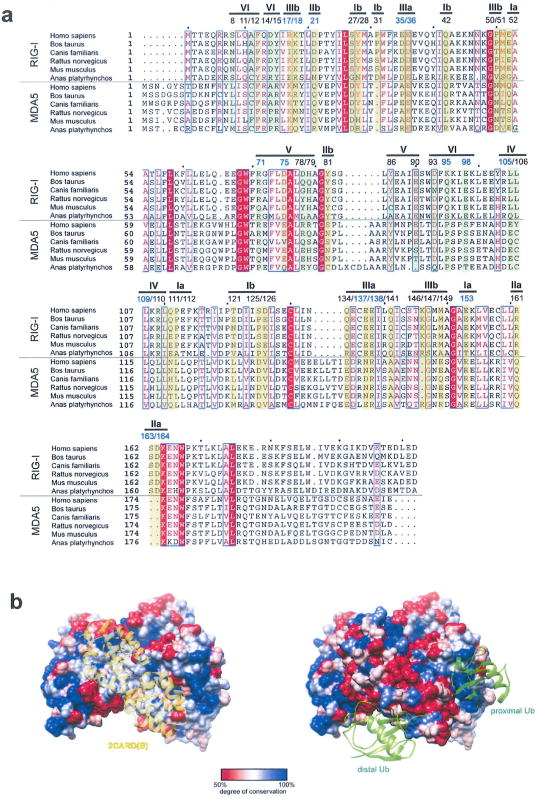
Extended Data Figure 8. Sequence conservation analysis of the 2CARD–2CARD and 2CARD–Ub interface.
a, Sequence alignment of RIG-I and MDA5 2CARD (using the program ClustalOmega27). Residues in RIG-I involved in the 2CARD–2CARD interactions (surface Ia/b–IIIa/b in Extended Data Fig. 4) and Ub binding (surface IV, V and VI in Extended Data Fig. 6), and their equivalent residues in MDA5 are highlighted (yellow and green for 2CARD–2CARD and 2CARD–Ub interfaces, respectively). Residue numbers right above highlights are according to human RIG-I. Residues tested by mutagenesis in this study are indicated by blue colour. Residues involved in the 2CARD–2CARD interactions show, on average, a moderate level of conservation in comparison to other residues on the surface of RIG-I 2CARD (see surface representation in b). Poor conservation of the tetramerization interface is consistent with previous observations that protein-protein interfaces often display evolutionary versatility due to the plasticity of the interaction and co-evolution of the interacting surfaces28,29. The Ub binding surface of RIG-I is more conserved than the 2CARD–2CARD interface (see surface representation in b), possibly reflecting the conserved nature of Ub. When the comparison is made between RIG-I and MDA5, we found that only four residues are well-conserved (F12 and L110 in the Ub-binding surface, and E36 and K164 in tetramerization surface), assuming interchange of residues within each group of F/Y, L/V/I or D/E as well-conserved. This is insufficient to support structural conservation of the 2CARD tetramer or 2CARD–Ub complex between RIG-I and MDA5. The structure of the MDA5 oligomers and/or MDA5–Ub complex would be required to compare 2CARD oligomerization mechanism between RIG-I and MDA5. b, Degree of sequence conservation (within RIG-I based on a) mapped onto the RIG-I 2CARD tetramer structure (generated using the program Chimera). Consistent with the analysis above, the 2CARD–2CARD interfaces show a moderate level of conservation, whereas Ub-binding sites show a higher degree of conservation. Other conserved surface areas may be involved in interactions with other molecules, such as TRIM25 or MAVS.