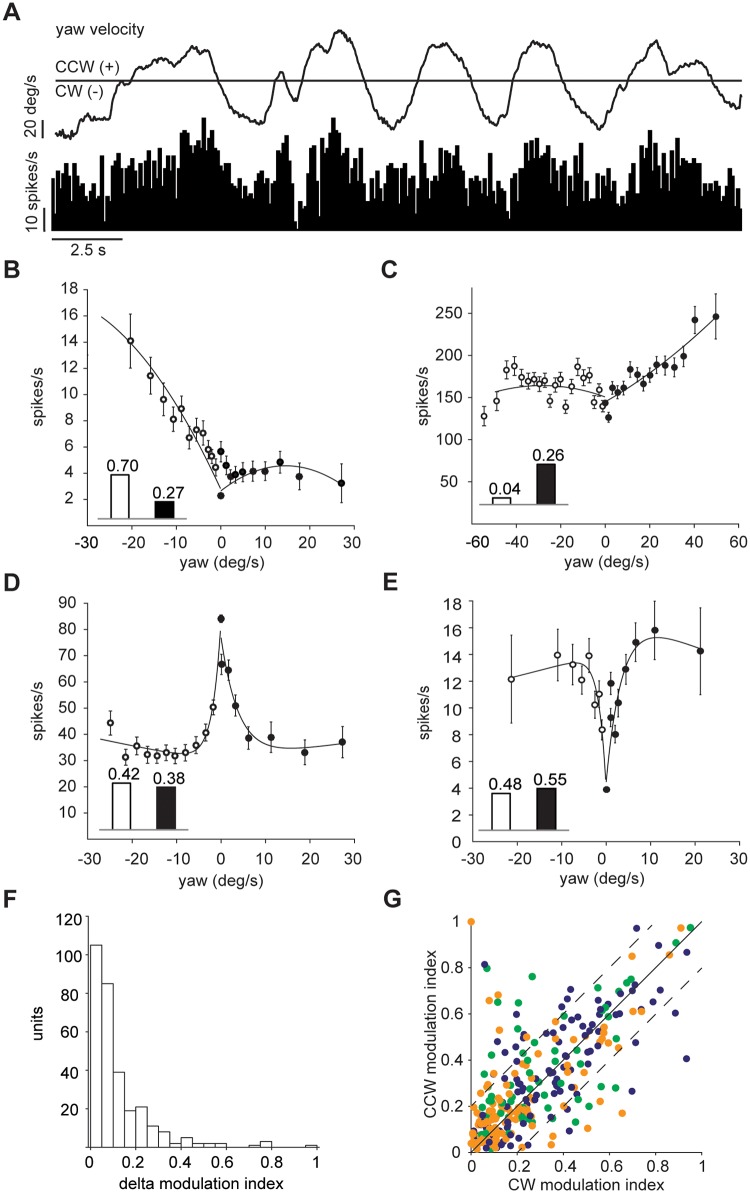
Fig 4. Cerebellar neuronal response to yaw direction.
(A) Example unit tuned to CCW yaw direction (positive): top, yaw trace in deg/s; bottom, mean instantaneous firing rate, bin width 100 ms. (B-C) Two example units preferentially responding to yaw-turning in the CW (B) or CCW (C) directions; each data point is formed from at least 900 bins (100ms width); error bars are s.e.m.; inset bars indicate the modulation index values derived from the two curves. (D) Example unit decreasing its activity in both yaw directions. (E) Example unit that increases its activity in either yaw direction. (F) Distribution of the difference in modulation index between the CW and CCW yaw direction. (G) Population plot of modulation index values of each unit for the CW and CCW direction (n = 310). Dashed lines show the threshold for units with difference in modulation index between the CW and CCW yaw direction larger than 0.2. Dot colour indicates cell class as in Fig 2.