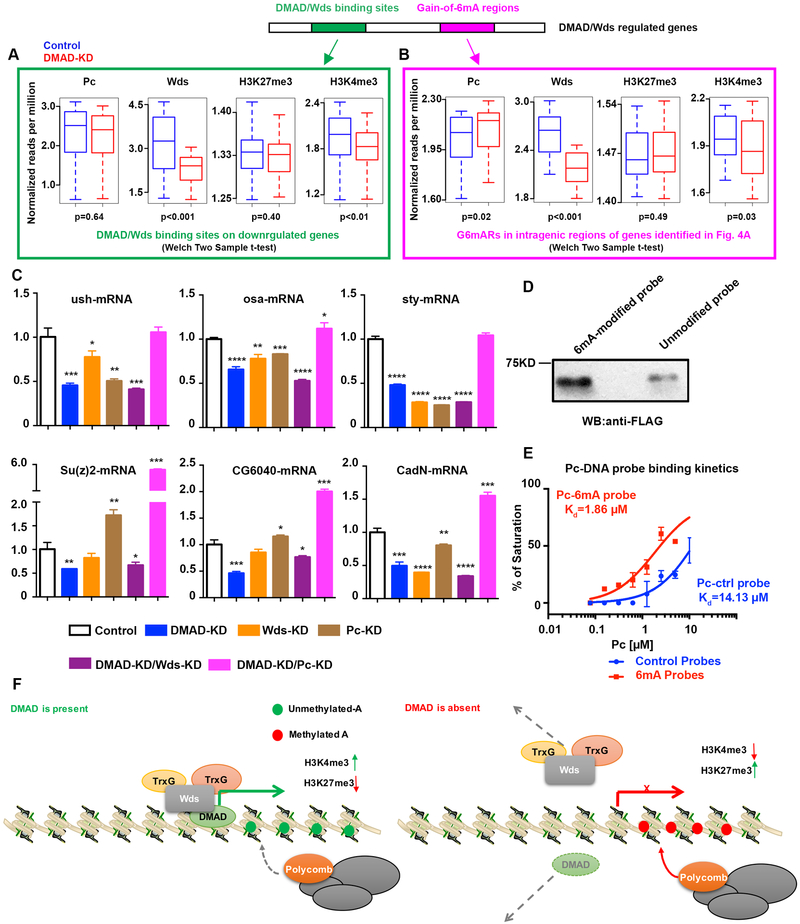
Figure 4. DMAD and 6mA coordinate with Trithorax and Polycomb.
(A) Average normalized reads (per million) dynamics in Pc, Wds, H3K27me3, and H3K4me3 at DMAD/Wds binding sites in genes downregulated in the absence of DMAD compared to the control are shown. Welch Two sample t-tests, p-values were indicated.(B) Average normalized reads (per million) dynamics in Pc, Wds, H3K27me3 and H3K4me3 at gain-of-6mA regions in intragenic regions of genes identified in Figure 4A that were bound by DMAD/Wds. Welch Two sample t-tests, p-values were indicated.(C) Loci from Figure 4A and 4B were further tested by qPCR for expression changes in the absence of DMAD, Wds, Pc, or combined depletion of DMAD and Pc, as well as DMAD and Wds. t-tests were performed. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001.(D) In vitro 6mA-Pc binding assays were performed to confirm direct correlation between 6mA and Pc.(E) Pc binding kinetics to control and 6mA-modified probes showed that Pc displayed stronger binding to 6mA-modified DNA probes, as measured by fluorescence polarization assays. (F) DMAD binds to a group of genes involved in neurodevelopment and neuronal functions. These genes are directly targeted by the Trithorax protein Wds to maintain an active transcription profile. Additionally, DMAD actively demethylates intragenic 6mA. In the absence of DMAD,Wds binding is reduced at these loci, and accumulation of intragenic 6mA recruits Polycomb proteins. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.