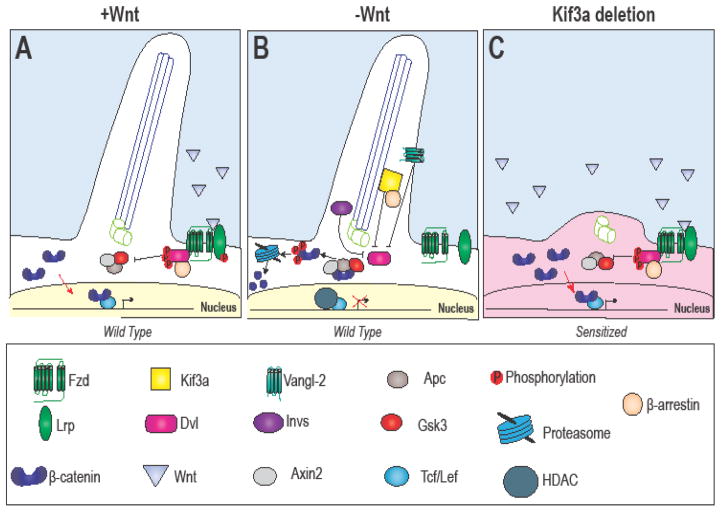
Figure 3. Hypothesized cilia-dependent Wnt signaling.
(A) Hypothesized (and controversial) activity of Wnt pathway components in the (A) presence and (B) absence of Wnt. (C) Loss of Kif3a causes increased translocation of β-catenin to the nucleus and increased target gene expression, thus “sensitizing” the cell to Wnt signaling.