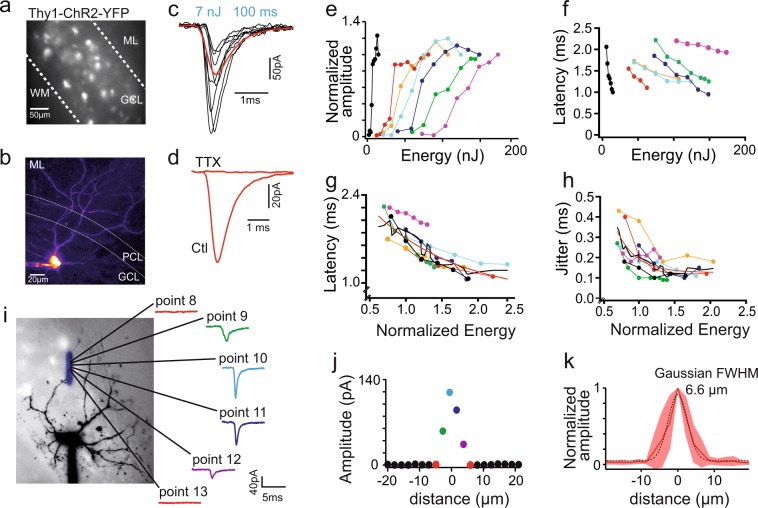
Figure 4.
Optogenetic stimulation of single mossy fibers with submilisecond precision and spatial precision of low-NA Gaussian beam stimulation. (a) Fluorescence image of cerebellar slice from the vermis of a Thy1-ChR2-YFP mouse that expresses ChR2 and YFP in a subset of mossy fibers. (b) Two-photon image of the Golgi cell filled with Alexa 594 (15 µM) via the recording pipette; GCL: granule cell layer, PCL: Purkinje cell layer; ML: molecular layer, WM: white matter. (c) Top panel: average EPSC (in red) evoked by the 100 µs stimulation with examples of single events (in black). (d) Light evoked events are action-potential dependent since the response disappears in the presence of TTX (200 nM). (e) Energy response curve recorded in Golgi cells (n = 7). (f) EPSCs latencies (in ms) as a function of energy for each cell (color code the same as in e); latencies measured on averages from 100 events, EPSCs delay decreased with increasing laser power. (g) Light evoked events latencies (as in f) as a function of energy which was normalized to the half activation value, extracted from sigmoidal fit applied to the recruitment curves in e; values of the fit: start 2.06 ms, tau: 1.197, base: 0.78 ms. Color code as in e and f. (h) Jitter, defined as the standard deviation of the latency, as a function of energy, normalized as described in g. Values of the fit: start 0.327 ms, tau: 0.273, base: 0.126 ms. Color code the same as in e–g. (i) two-photon image of the Golgi cell recorded during spatial resolution experiment with the drawing of the accurate position of the stimulated points (superimposed in blue). The center of each point is marked with a black dot. On the right, examples of the evoked EPSCs in one cell showing no response (point 8 and point 13), response evoked at the edge of the mossy fiber (before and after the hotspot, point 9 and 12, respectively) and hotspot stimulation in point 10 and 11. Note decreased latency of the events at the hotspot in comparison to the spot located at the edge of the fiber. (j) Graph showing the amplitude of the evoked EPSCs as a function of distance for the example cell in c; colors of the spots on the graph correspond to the points in a. k. Summary graph showing the relative amplitude (normalized to the maximal amplitude for each cell) of the evoked events as a function of distance, zeroed at the hotspot (maximal evoked amplitude). Shaded area around the average (solid red line) represents ± s.d.; n = 8.