Figure 1.
Whole-Genome RNAi Screening Strategy to Identify Cell-Fate-Safeguarding Factors in C. elegans
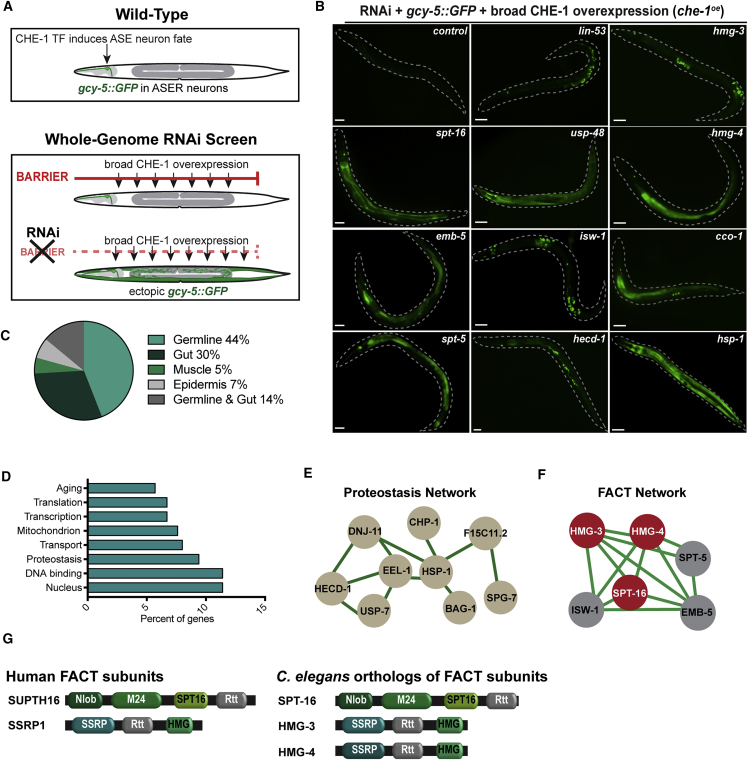
(A) Schematic representation: the ASER neuron is labeled by gcy-5::GFP. Overexpression of the Zn-Finger TF CHE-1 (che-1oe) combined with genome-wide RNAi led to discovery of genes preventing ectopic gcy-5::GFP induction in adults.
(B) Representative images of control animals, GFP induction in germline (lin-53, hmg-3, isw-1, and hecd-1 RNAi), intestine (spt-16, hmg-4, emb-5, and spt-5 RNAi), epidermis (hsp-1 RNAi), or germline and gut simultaneously (cco-1). Dashed lines indicate outline of animals. Scale bars represent 20 μm.
(C) Percentage of 171 genes whose knockdown allowed ectopic GFP induction in specific tissues.
(D) Gene ontology (GO) categories of genes from the screen.
(E and F) Proteostasis and FACT protein network based on genes identified in the screen. Network plots are based on known and predicted interactions from STRING (string-db.org) with minimal confidence score of 0.4. FACT complex proteins are highlighted in red.
(G) Models of FACT subunits in human and C. elegans. Conserved protein domains according to Pfam and InterPro are indicated: Nlob, N-terminal lobe domain; M24, metallopeptidase family M24; SPT16, FACT complex subunit Spt16p/Cdc68p; Rtt, histone chaperone Rttp106-like; SSRP1,structure-specific recognition protein; HMG, high mobility group box domain.
See also Table S1.