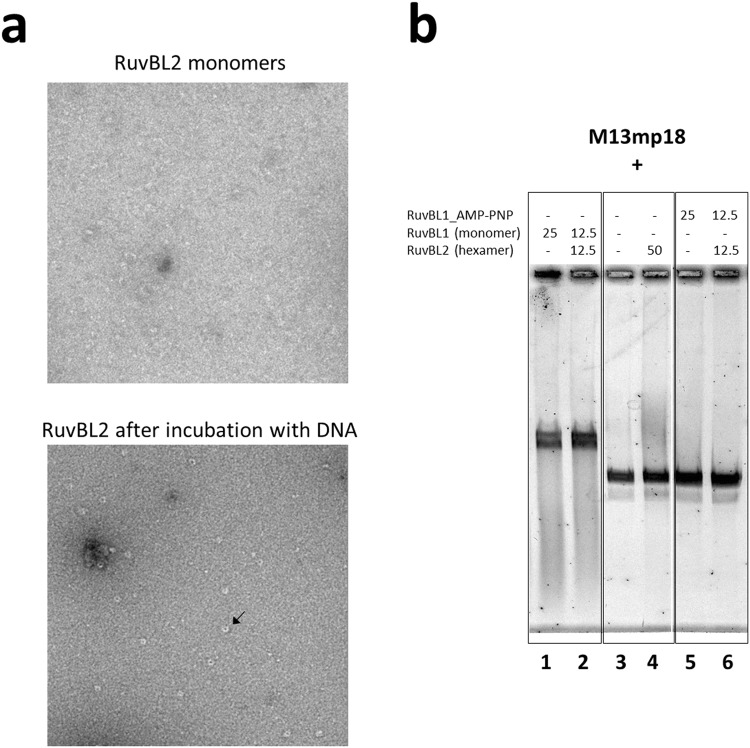
Figure 6.
hsRuvBL2 interaction with DNA. (a) Interaction of monomeric hsRuvBL2 with ssDNA promotes ring reassembly, as observed by negative-staining EM. The black arrow highlights an hsRuvBL2 ring. An electrophoretic mobility shift assay (b) shows that hexameric hsRuvBL2 did not bind to ssDNA (lane 4), as there is no shift in running distance when comparing to the one observed by DNA alone (lane 3). However, when co-incubated in equimolar amounts with hsRuvBL1 (lane 2), there is a shift that indicates protein binding. Since this shift is equivalent to the one observed when incubating a total molar amount of only hsRuvBL1 (lane 1), we surmise that hsRuvBL2 is also bound to DNA in the former, most likely mediated by hsRuvBL1. Lanes 5 and 6 show no such binding in the presence of AMP-PNP, indicating that this non-hydrolysable nucleotide somehow prevents DNA binding.