FIGURE 1.
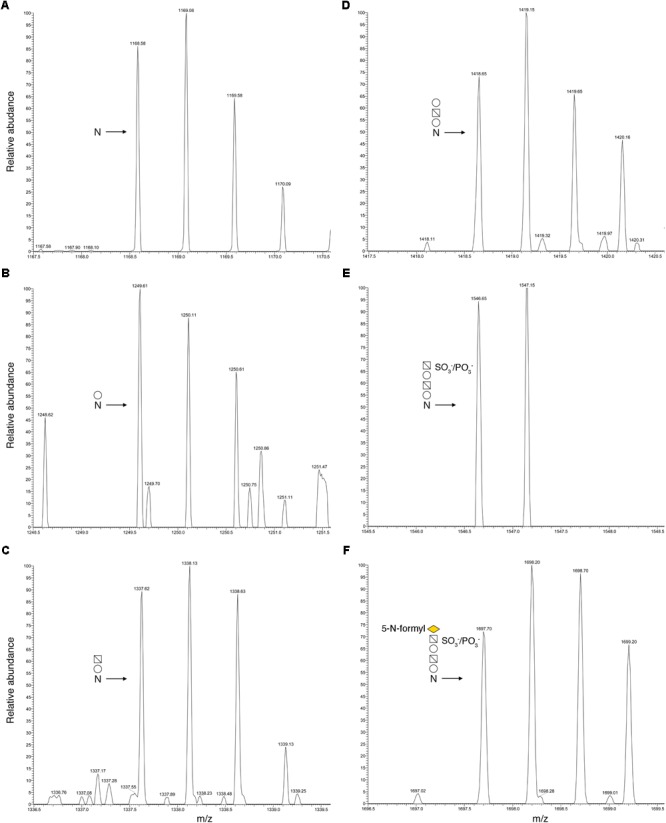
N-glycosylation profile of Halorubrum sp. PV6 S-layer glycoprotein Asn-94. LC-ESI/MS analysis of the Asn-94-containing peptide derived from the Halorubrum sp. PV6 S-layer glycoprotein following digestion with trypsin and GluC protease was performed. Shown are doubly charged [M+2H]2+ ion peaks corresponding to (A) the 78TGSYAIGGPDAADGAFNVTVVTPR101 peptide (m/z 1168.58), and the same peptide successively modified by (B) a hexose (m/z 1249.61), (C) a hexuronic acid (m/z 1337.62), (D) a hexose (m/z 1418.65), (E) a sulfated/phosphorylated hexuronic acid (m/z 1546.65), and (F) a 5-N-formyl-legionaminic acid (m/z 1697.70). In each panel, the N-glycosylation status of the peptide is schematically depicted, where “N” corresponds to Asn-94. Employing symbol nomenclature for glycans guidelines (Varki et al., 2015), open circles correspond to hexoses, open squares containing a diagonal correspond to hexuronic acids, and the yellow diamond corresponds to 5-N-formyl-legionaminic acid.
