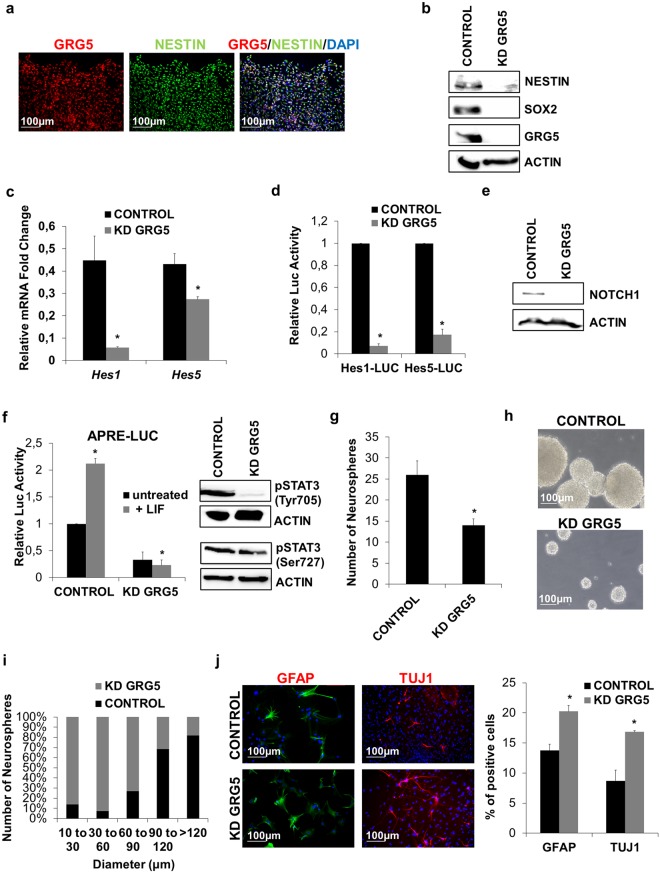
Figure 6.
GRG5 severely contributes to embryonic NSC identity maintenance. (a) Immunofluorescence staining for GRG5 and NESTIN in embryonic NSCs cultured in monolayer conditions. (Scale bar, 100 μm) (b) Protein levels of stemness factors in CONTROL and KD GRG5 NSCs. (c) Relative mRNA levels of the Notch mediators Hes1 and Hes5 in CONTROL and KD GRG5 NSCs. Mean + SD of n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 (d) Notch signaling is down-regulated in the absence of GRG5. Luciferase assay monitoring the activity of Notch pathway in CONTROL and KD GRG5 NSCs. Data are shown as Mean + SD of n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05. (e) Protein levels of NOTCH1 receptor in CONTROL and KD GRG5 NPCs. (f) Luciferase assay showing decreased STAT3 binding activity and western blot showing reduced protein level of p-STAT3 (Tyr705 and Ser727) in KD GRG5 NSCs. Mean + SD of n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 (g) Neurosphere forming assay comparing CONTROL and KD GRG5 NSCs. Six days upon cell culture in proliferation medium, the total number of the formed neurospheres was counted. Mean + SD of n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 h) Phase-contrast images showing CONTROL and KD GRG5 neurospheres (Scale bar, 100 μm). (i) Comparison of CONTROL and KD GRG5 NSC proliferation capacity by measuring the size of the generated neurospheres. Mean of n = 3 independent experiments. (j) Loss of GRG5 facilitates NSC specification. Immunofluorescence staining for the astrocytic marker GFAP and the neuronal marker TUJ1 in CONTROL and KD GRG5 NSCs five days upon culture in differentiation medium (scale bar, 100 μm). Mean + SD of n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05.