FIGURE 1.
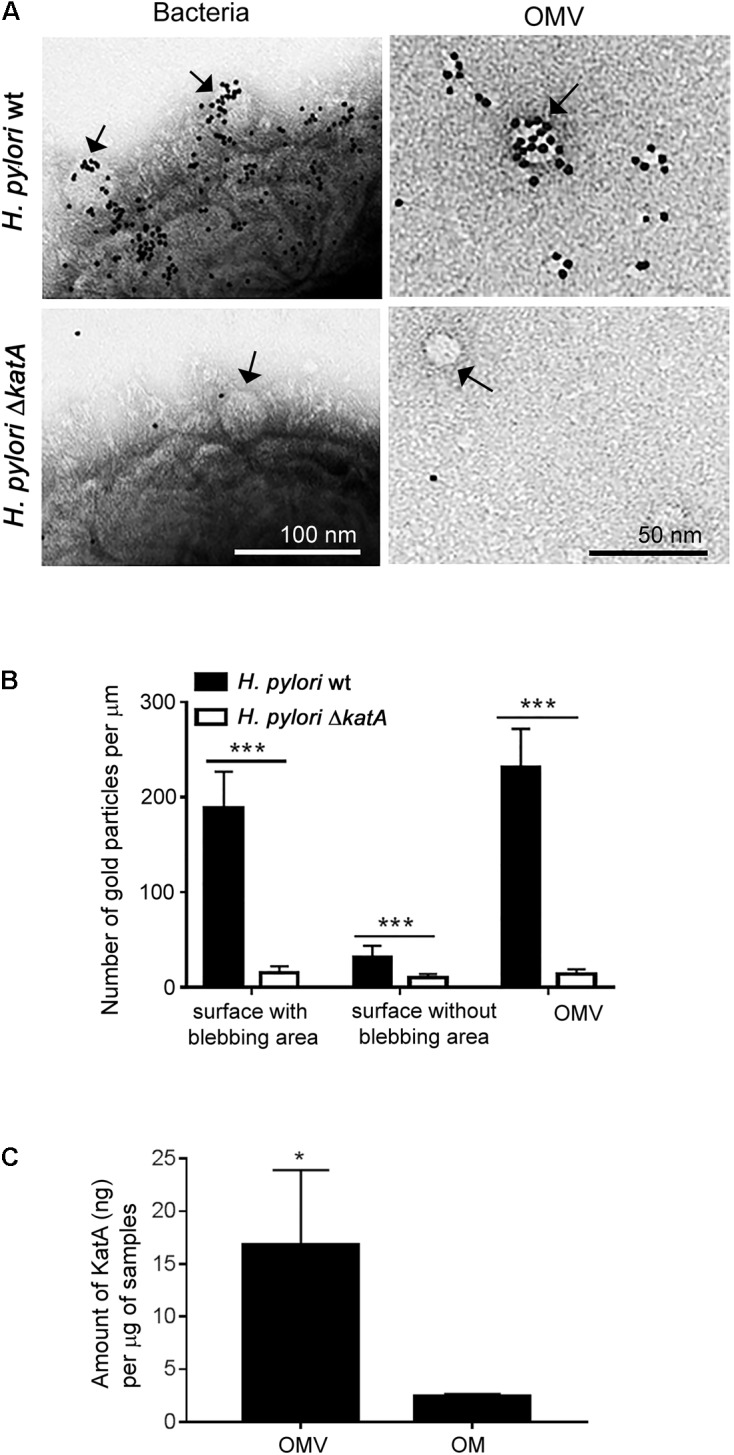
Characterization of KatA enrichment and deposition at the surface of Helicobacter outer membrane vesicles (OMVs). (A) Detection of KatA at the surface of OMVs by immunoelectron microscopy using gold conjugated rabbit anti-KatA IgG pAb (black particles) at the outer surface of intact H. pylori 18943 wt (upper panel) or at the outer surface of the KatA-deficient mutant H. pylori 18943ΔkatA (lower panel). Arrows indicate OMVs that are vesiculating from the “blebbing area” at the bacterial surface (left panels) or purified OMVs (right panels). Visualization by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) was performed on a Philips/FEICM 100 TWIN transmission electron microscope, and images were documented with a side-mounted Olympus Veleta camera having a resolution of 2048 × 2048 pixels (2k × 2K) and ITEM acquisitions software. (B) KatA is accumulated in OMVs at the bacterial surface, and in the released OMV fraction. The number of anti-KatA IgG pAb-gold particles per μm from 50 randomly selected TEM image profiles were calculated, and corresponded to at least 1000 different bacteria. (C) A significantly higher concentration of KatA is present in OMVs compared to the OM fraction. Estimation of KatA concentrations in OM and OMVs was done by western blotting as shown in Supplementary Figure S1. For (B) and (C), statistical differences were calculated by two-way ANOVA and two-tailed Student’s t-test, respectively (mean ± SD; n = 3; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
