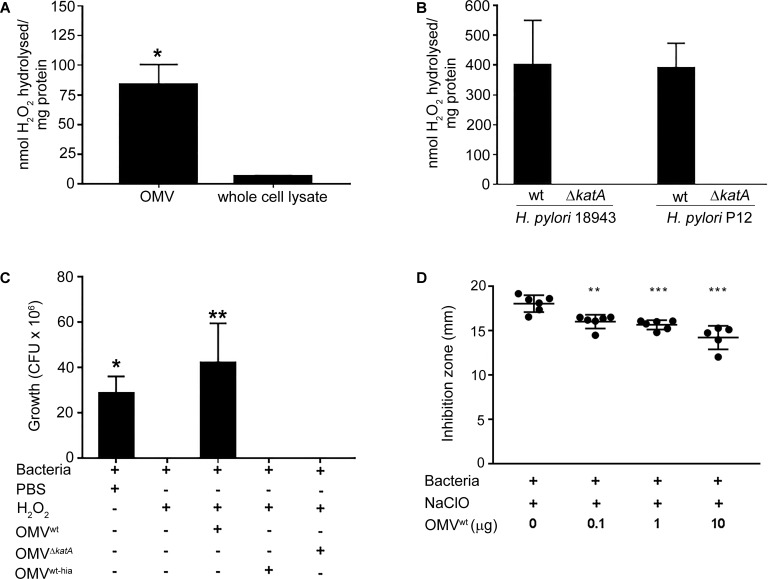
FIGURE 2.
OMVs carrying KatA hydrolyse/detoxify ROS and provide protection against ROS-mediated bacterial killing. (A) Comparison of catalase activity between OMVs derived from H. pylori 18943 wt and a bacterial lysate. An increased H2O2 hydrolysis on a weight basis was detected with OMVs compared to bacterial lysate. (B) Determination of KatA-dependent catalase activity in OMVs. Deletion of KatA in two different strains of H. pylori, 18943 and P12 resulted in abolished catalase activity in OMVs from H. pyloriΔkatA mutant strains compared to OMVs derived from the wild type counterparts. In (A) and (B), catalase activity was presented as nmol of H2O2 decomposed per mg of sample tested (mean ± SD; n = 3; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01). (C) and (D), Helicobacter OMVs reduce the bactericidal activity of H2O2 and NaClO, and thus promoted bacterial survival. In (C), H. pylori P12ΔkatA devoid of catalase activity was challenged with 1 mM H2O2 preincubated with 40 μg/ml of OMV (equivalent to OMVs produced from 109 CFU) (OMVwt, OMVΔkatA or heat-inactivated OMVs; OMVhia). In (D), H. pylori 18943ΔkatA devoid of KatA expression was exposed to 5% NaOCl that had been pre-treated with 0.1–10.0 μg of OMVwt. Pure H2O2 and NaOCl in PBS that were fully bactericidal were included as a positive control. In (C), the viability of bacteria was assessed by plating and counting colony forming units (CFU). Only KatA-containing OMVwt was able to neutralize H2O2 and promote survival of H. pylori P12ΔkatA from peroxidative killing. OMV lacking KatA (OMVΔkatA) or heat-inactived KatA (OMVhia) did not show any protection of whole bacteria (mean ± SD; n = 3; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01). In (D), the bactericidal activity of NaOCl was decreased by preincubation with increasing amounts of OMVwt (equivalent to OMVs produced from 0.2 to 2 × 108 CFU). The killing of H. pylori 18943ΔkatA by NaOCl was measured by the diameter of inhibition zone, which is the area without bacterial growth (mean ± SD; n = 3; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001).