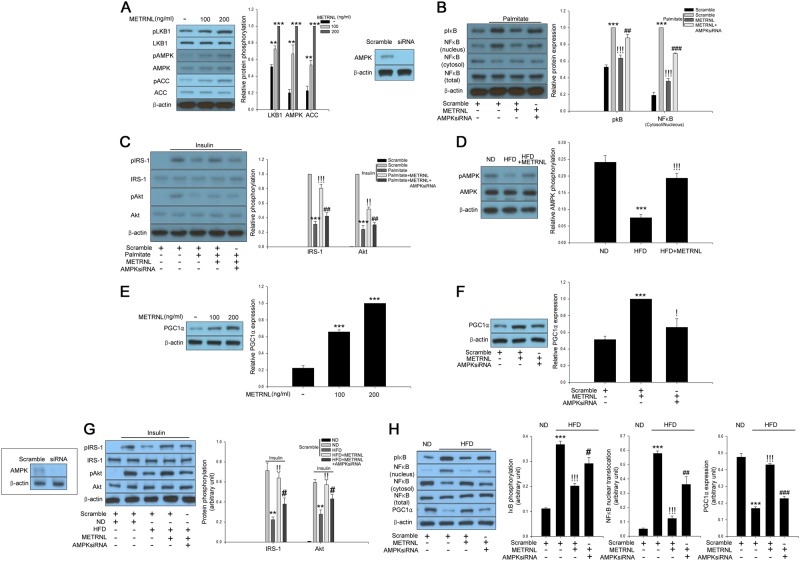
Fig. 4. METRNL ameliorates inflammation and insulin resistance via an AMPK-mediated pathway.
a Western blot analysis of LKB1, AMPK, and ACC phosphorylation in differentiated C2C12 cells treated with METRNL (0–200 ng/mL) for 24 h. b Confirmation of AMPK siRNA efficiency in differentiated C2C12 cells. Western blot analysis of palmitate (200 μM)-induced inflammation markers in AMPK siRNA (20 nM)-transfected differentiated C2C12 cells treated with METRNL (0–200 ng/mL) for 24 h. c Western blot analysis of the palmitate-induced impairment of IRS-1 and Akt phosphorylation in AMPK siRNA-transfected differentiated C2C12 cells treated with METRNL (0–200 ng/mL) for 24 h. Human insulin (10 nM) was used to stimulate insulin signaling for 3 min. d Western blot analysis of AMPK phosphorylation in soleus muscle of mice treated with HFD and METRNL (5 animals/treatment group). e Western blot analysis of PGC1α expression in differentiated C2C12 cells treated with METRNL (0–200 ng/mL) for 24 h. f Western blot analysis of METRNL (200 ng/mL)-induced PGC1α expression in AMPK siRNA (20 nM)-transfected differentiated C2C12 cells for 24 h. Confirmation of AMPK siRNA efficiency in skeletal muscle of mice. Western blot analysis of IRS-1 and Akt phosphorylation (g), and inflammatory markers (h) in AMPK siRNA-transfected skeletal muscle of experimental mice. Means ± SEM were obtained from three separate experiments or five animals. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, and *P < 0.05 compared to control or ND treatment.!!!P < 0.001 and !!P < 0.01 compared to palmitate or HFD treatment. ###P < 0.001, ##P < 0.01, and #P < 0.05 compared to palmitate plus METRNL treatment or HFD plus KA group