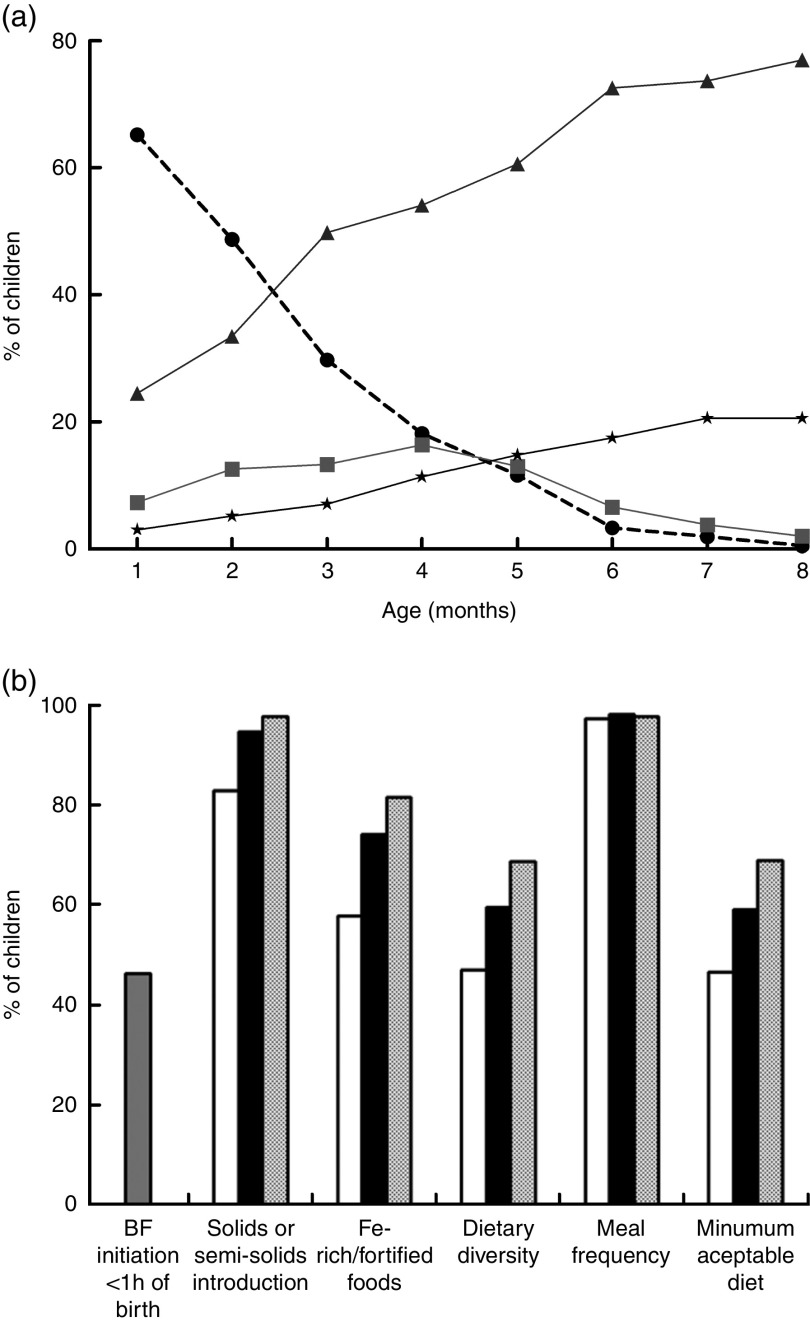
Fig. 1.
Breast-feeding patterns* and WHO core indicators on infant and young child feeding† in the Brazilian MAL-ED cohort site (n 233): (a) breast-feeding practices from 1 to 8 months of age ( , exclusive breast-feeding;
, exclusive breast-feeding;  , predominant breast-feeding;
, predominant breast-feeding;  , partial breast-feeding;
, partial breast-feeding;  , no breast-feeding); (b) breast-feeding (BF) initiation within 1 h of birth (
, no breast-feeding); (b) breast-feeding (BF) initiation within 1 h of birth ( ), solids or semi-solids introduction, iron-rich/fortified foods, dietary diversity, meal frequency and minimum acceptable diet from 6 to 8 months of age (
), solids or semi-solids introduction, iron-rich/fortified foods, dietary diversity, meal frequency and minimum acceptable diet from 6 to 8 months of age ( , 6 months;
, 6 months;  , 7 months;
, 7 months;  , 8 months). *Exclusive breast-feeding: breast-feeding with no other foods or liquids given (not even water) over the previous 24 h period, except for drops or syrups containing vitamins, mineral supplements or medicine. Predominant breast-feeding: breast-feeding with the introduction of plain water or water-based liquids, such as tea or juice. Partial breast-feeding: breast-feeding with the inclusion of other milks, formula and/or semi-solids. †Dietary diversity: ≥4 different food groups. Meal frequency: ≥2 meals/d for breast-fed infants and ≥4 meals/d for non-breast-fed infants. Minimum acceptable diet: when dietary diversity and meal frequency are achieved
, 8 months). *Exclusive breast-feeding: breast-feeding with no other foods or liquids given (not even water) over the previous 24 h period, except for drops or syrups containing vitamins, mineral supplements or medicine. Predominant breast-feeding: breast-feeding with the introduction of plain water or water-based liquids, such as tea or juice. Partial breast-feeding: breast-feeding with the inclusion of other milks, formula and/or semi-solids. †Dietary diversity: ≥4 different food groups. Meal frequency: ≥2 meals/d for breast-fed infants and ≥4 meals/d for non-breast-fed infants. Minimum acceptable diet: when dietary diversity and meal frequency are achieved