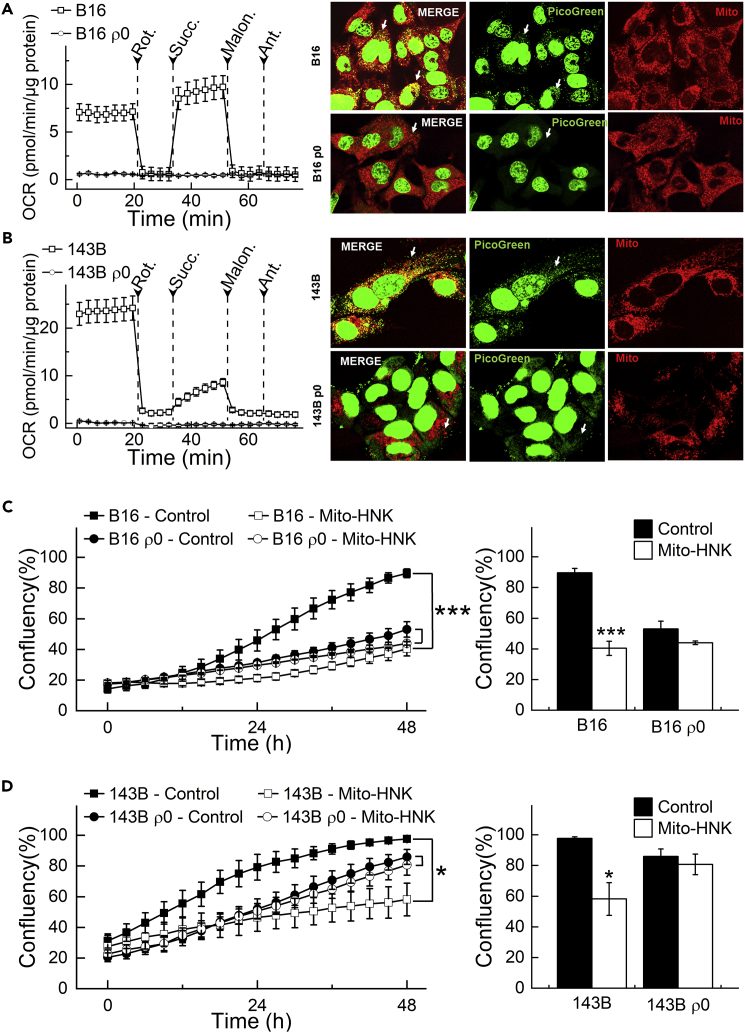
Figure 5.
Depletion of mtDNA Abrogates the Anti-Proliferative Effects of Mito-HNK in Lung Cancer Cells
(A and B) Validation of the loss of activities of the mitochondrial complexes in ρ0 cells. (A and B, left panels) Permeabilized cells were assayed in medium containing 10 mM pyruvate and 1.5 mM malate (substrates for complex I) in mannitol and sucrose (MAS) buffer. The complex I-related oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was assayed immediately and verified by injecting rotenone (complex I inhibitor) as indicated. Then, complex II-related OCR was measured by supplying cells with succinate (substrate for complex II, 10 mM). Both malonate (complex II inhibitor, 10 mM) and antimycin A (complex III inhibitor, 20 μM) were injected where indicated. (A and B, right panels) Validation of the absence of mitochondria in ρ0 cells with PicoGreen staining for mtDNA. Arrows indicate mitochondria fibrillar network.
(C and D) mtDNA depletion abrogates the anti-proliferative effects of Mito-HNK (0.4 μM, 48 hr) in both B16 and 143B ρ0 cells. (***P < 0.001 vs. B16 or 143b parental cells). Error bars indicate SD.