Figure 8.
Proposed Mechanisms of the Antiproliferative and Anti-invasive Effects of HNK and Mito-HNK
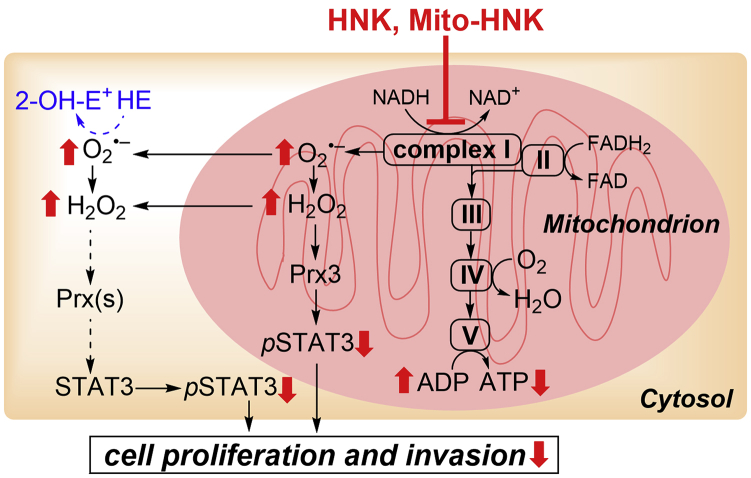
NADH dehydrogenase (complex I) plays a key role in regulating and maintaining mitochondrial function and energy production (ATP). Suppressing complex I activity can increase ROS production and signaling through ROS-associated pathways. We propose that one potential mechanism of action of Mito-HNK is that it inhibits complex I in lung cancer cells; stimulates ROS generation, which promotes oxidation of mitochondrial Prx3; activates AMPK; and inhibits STAT3ser727 phosphorylation and cell proliferation. The results indicate that Mito-HNK mediates these events more robustly and at much lower concentrations than does HNK.