Figure 1.
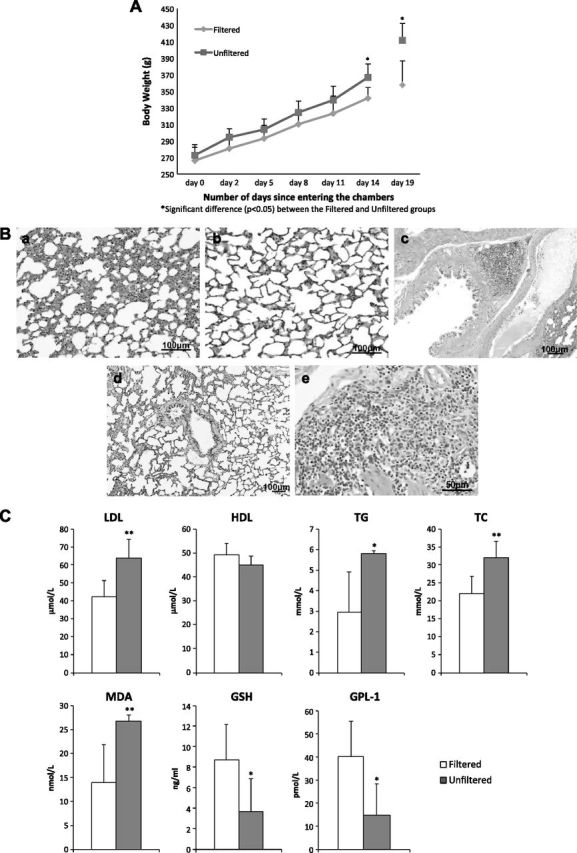
Pregnant rats exposed to unfiltered Beijing air vs. those exposed to filtered Beijing air. A) Body mass measured from d 0, when rats went into chambers, to d 14 (in first set of experiments) and measured at d 19 (in second set of experiments). Error bars represent ±sd. B) Lung histology (hematoxylin and eosin stain) showing inflammation in alveoli of rat after 19 d exposure to unfiltered air (a), but no apparent inflammation in alveolus of rat after 19 d filtered air exposure (b). Similar histologic evidence for inflammation in bronchus of unfiltered air exposed rat (c) in reference to that of filtered air exposed rat (d). Higher-magnification micrograph indicates that inflammatory cells are mainly mononuclear cells (e). C) Blood biomarkers measured in pregnant rats after 19 d exposure protocol. Significant differences between groups are indicated. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
