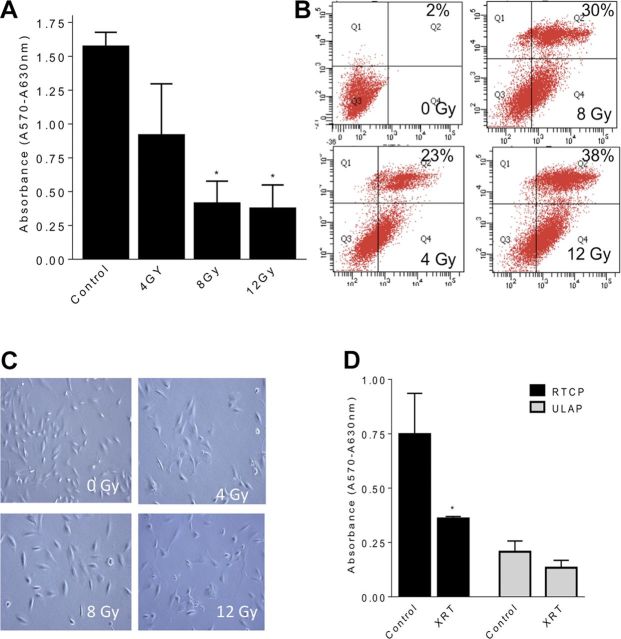
Figure 1.
Effect of ionizing radiation on viability of human renal podocytes. Metabolic activity was assessed by MTT assay, and results are indicated relative to control cells (no radiation). A) Differentiated podocytes were irradiated at 0, 4, 8, or 12 Gy, and MTT assay was carried after 24 h. B) Apoptosis was quantified by annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining followed by flow cytometry. Annexin V and PI values for each treatment were plotted on the x and y axis, respectively. Shown are the percentage cells of each treatment group in top right quadrant (annexin V+, PI+). C) Podocytes were grown on 10-cm dishes and irradiated at 0, 4, 8, or 12 Gy. Cell morphology was examined under an inverted light microscope equipped with a CCD camera using an ×20 objective. Representative images are shown. D) Podocytes were irradiated (8 Gy) and incubated for 24 h at 37°C into wells of 6-well regular tissue culture plates (RTCPs) or ULAPs. Results shown are the mean values of 3 different experiments each performed in triplicate, with error bars indicating sem from multiple experiments. *P < 0.05.