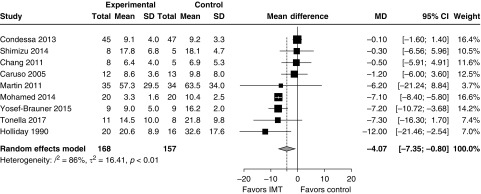
Figure 3.
Impact of inspiratory muscle training (IMT) on the duration of ventilation in mechanically ventilated patients. After exclusion of studies at serious risk of bias, the treatment effect was no longer significant (mean difference, 4.6 d; 95% CI, −1.0 to 10.1 d; I2 = 94%). Weight refers to the contribution of each study to the meta-analysis estimate of effect. CI = confidence interval; MD = mean difference; SD = standard deviation.