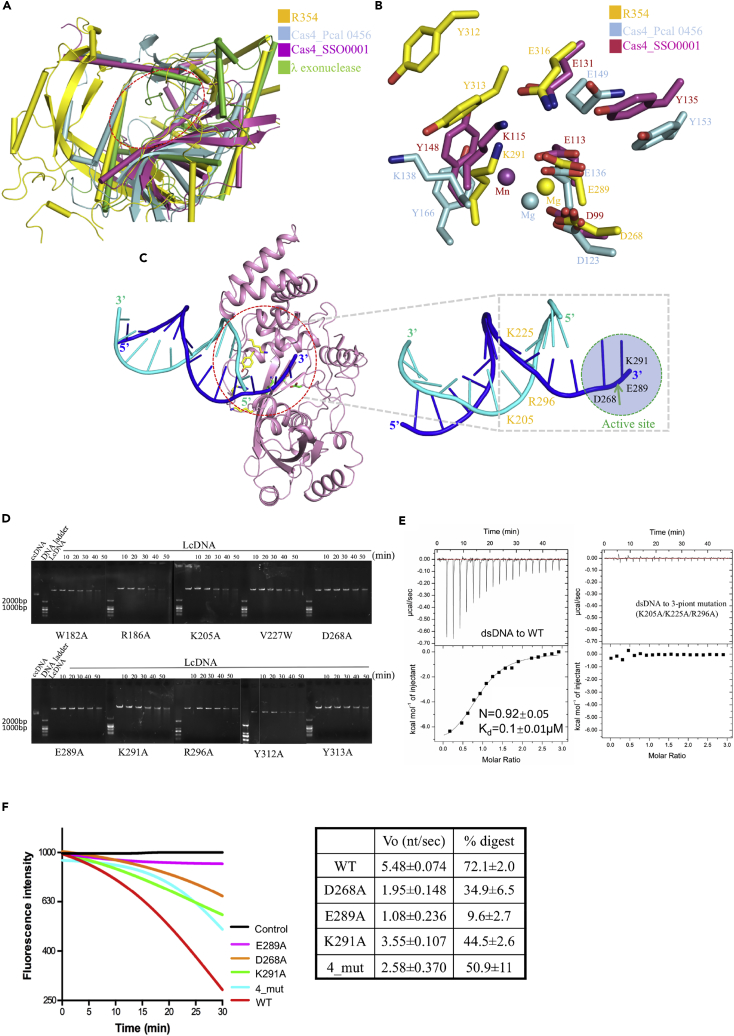
Figure 6.
Structural Analysis
(A) Structural comparisons of R354, Cas4_Pcal 0456, Cas4_SSO0001, and λ exonuclease. The similarities between the core catalytic domains of the four proteins are highlighted by red dashed lines.
(B) Comparison of active sites of R354 and Cas4; some residues are conservative in both active sites, which suggests that R354 has similar function to Cas4.
(C) A cartoon presentation of the dsDNA modeled into the structure of R354 (blue for the cleaved strand with the 3′-OH and cyan for the other strand), which shows interactions between DNA and R354. DNA was modeled by superimposing the catalytic core domain of R354 and λ exonuclease (PDB ID 3SM4Zhang et al., 2011). The red dotted ring is interpreted in the right panel. Residues putatively interacting with the DNA substrate and involved in catalytic reaction are shown as sticks in the left panel. The cut site of DNA strand and the active site of R354 are indicated with highlighted label; the key residues are labeled in the right panel.
(D) Verification of key residues involved in R354 enzymatic activity using activity assays. LcDNA refers to linear coiled-coil DNA; ccDNA refers to circular coiled-coil DNA.
(E) Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) measurement of dsDNA binding. Representative ITC raw data and binding trace for dsDNA titrated into the solution containing wild-type (WT) R354 in the left panel: Kd = 0.1 ± 0.01 μM; N = 0.92 ± 0.05. The variant harboring three point mutations (K205A/K22A/R296A) can disrupt the dsDNA binding in the right panel.
(F) Quantitative exonuclease assays. (Left) Comparison of exonuclease activities of wild-type and representative variants of R354. The reactions began to record (m = 0) at the signal stabilized by the addition of enzyme to reaction buffer. (Right) The reaction parameters are shown in the table. The first column indicates the rate determined by the initial slope of the reaction. The percent of DNA substrate digested at 30 min is shown in the second column by comparison of detected fluorescence relative to reactions between positive (WT) and negative controls. Data are measured with three independent replicates for standard errors.