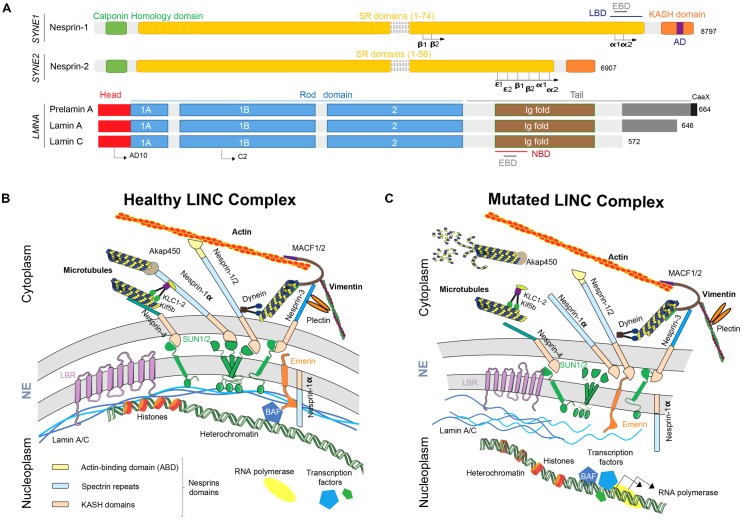
FIGURE 1.
Nesprins and lamins as part of the LINC complex. (A) Nesprins and lamins isoforms structures. AD, adaptive domain; EBD, emerin binding domain; KASH domain, Klarsicht/ANC-1/Syne Homology; LBD, lamin binding domain; NBD, nesprin binding domain; SR, spectrin repeats. (B) The healthy LINC complex and its interactors. Nesprins play multiple functions at ONM but also at INM. Full-length nesprins take part at the ONM to the bridge linking the nucleus to the actin cytoskeleton and shorter isoforms, such as nesprin-1a, interact via Akap450 and KLC-1/2 with microtubules. At the same time, smaller isoforms interact with the nucleoskeleton at INM. (C) When a mutation affects LMNA or SYNE genes, the disruption of the LINC complex participates to the physiopathogenesis of the diseases by structural defects, nuclear migration and anchoring defects and cell signaling pathways and gene expression regulation defects. NE, nuclear envelope; LINC, linker of nucleoskeleton to cytoskeleton; ONM, outer nuclear membrane; INM, inner nuclear membrane; KASH domain, Klarsicht/ANC-1/Syne homology; SUN, Sad1p/UNC84; BAF, barrier to auto-integration factor.