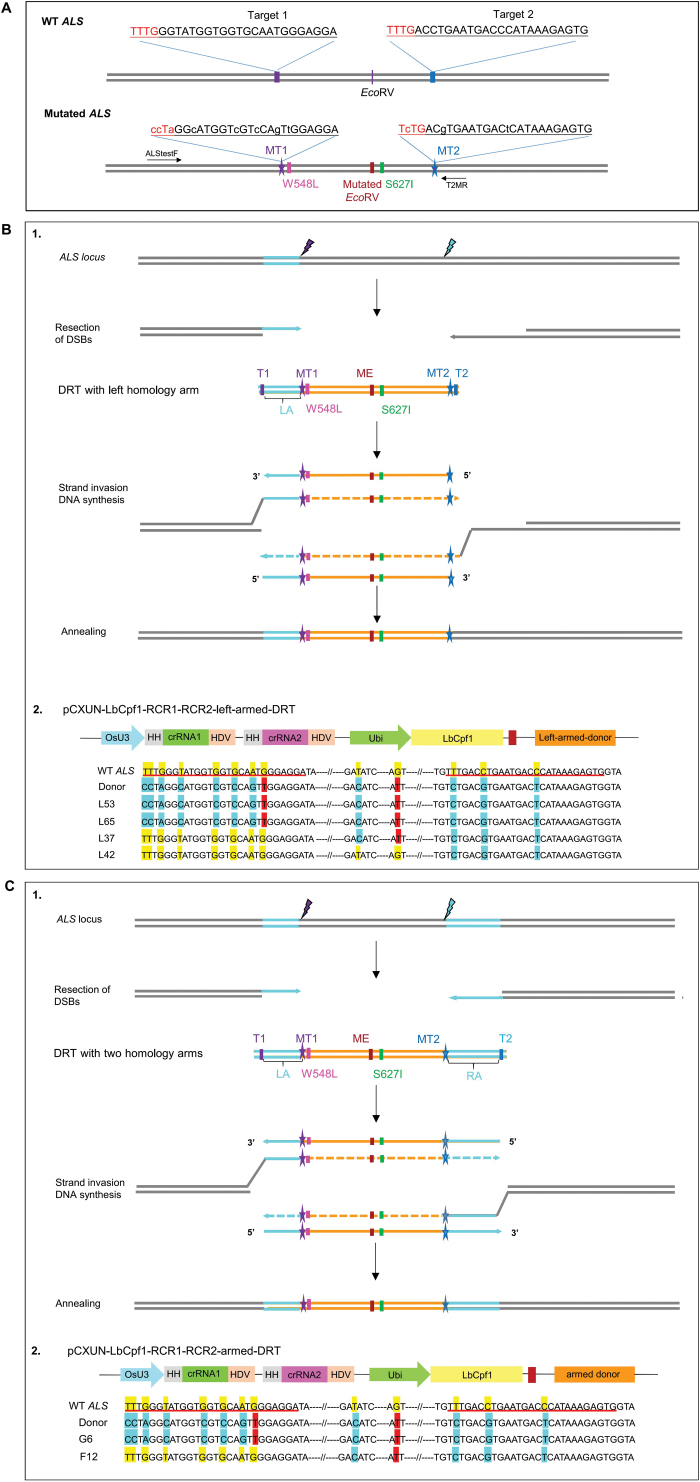
Fig. 1.
Homology-directed repair (HDR) of double strand breaks (DSBs) generated by the LbCpf1 endonuclease in rice. (A) A schematic description of HDR-mediated precise gene replacement in rice. A wild-type (WT) ALS gene fragment is removed by LbCpf1 and a couple of crRNAs. The LbCpf1 target sequences are underlined, and the PAM sites and the mutated PAM sites are underlined and highlighted in red. The WT ALS fragment is replaced by a mutant version that introduces changes of two discrete amino acid residues. The PAM sites and an EcoRV site are modified to prevent the replacement from further cleavage by LbCpf1/crRNAs and to facilitate detection of gene replacement events, respectively. (B) CRISPR/Cpf1-mediated HDR in rice calli using vector pCXUN-LbCpf1-OsU3-RCR1-RCR2-left-armed-DRT co-introduced with free left armed-DRT through CRISPR/Cpf1-mediated HDR. (B-1) A schematic description of the synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA) pathway of HDR with the donor containing only the left homology arm. Each line corresponds to a DNA strand. Chromosomal DNA is in gray, DRT in orange, homology arms of DRT are in blue, and arrows refer to the 3' ends. T1, target 1; T2, target 2; MT1, mutated PAM site and mutated target 1; MT2, mutated PAM site and mutated target 2; LA, left arm; ME, mutated EcoRV. Resecting DSB creates 3' overhangs on each side of the DSB. The overhangs in the 3' end pair with complementary strands in the DRT and are extended. The newly synthesized strands withdraw from the donor and anneal back at the locus. (B-2) Sequence analyses of the representative HDR events. PCR products were amplified by allele-specific primer set ALStestF/T2MR as described in (A). The calli L53 and L65 had undergone precise HDR, whereas the calli L37 and L42 had undergone partial HDR. The sequences shadowed in yellow and blue represent the same bases as those of the wild type and the designed DRT, respectively. Specifically, the sequences shadowed in red indicate the expected targeted substitution. (C) CRISPR/Cpf1-mediated HDR in rice calli using vector pCXUN-LbCpf1-OsU3-RCR1-RCR2-armed-DRT co-introduced with free armed-DRT through CRISPR/Cpf1-mediated HDR. (C-1) A schematic description of the synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA) pathway of HDR with a DRT containing two homologous arms. In this, and all other schematics, each line corresponds to a DNA strand. Chromosomal DNA is indicated in gray, DRT is in orange, the homology arms are in blue, and arrows indicate the 3' ends. T1, target 1; T2, target 2; MT1, mutated PAM site and mutated target 1; MT2, mutated PAM site and mutated target 2; LA, left arm; RA, right arm; ME, mutated EcoRV. (C-2) Sequence analyses of the representative HDR events. PCR products were amplified by allele-specific primer set ALStestF/T2MR as described in (A). The callus G6 had a precise HDR, whereas the callus F5 had undergone partial HDR. The sequences shaded in yellow and blue represent the wild-type and the designed donor repair template, respectively. Specifically, the sequences shaded in red indicate the expected targeted substitutions.