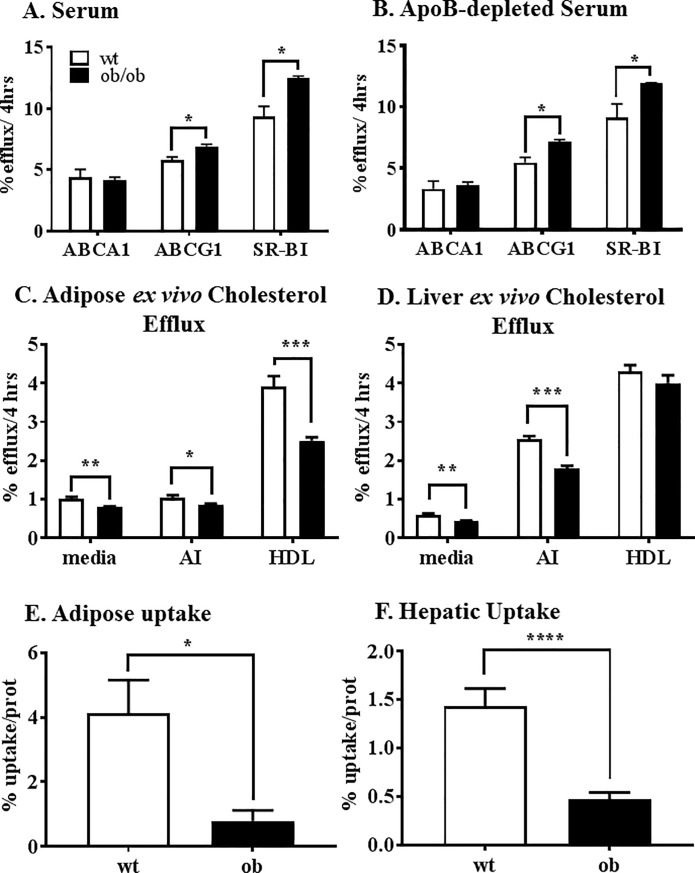
Fig 4. Cholesterol efflux potential of the serum and adipose and liver ex vivo cholesterol efflux capacity and cholesterol uptake of ob/ob and wt mice.
Serum (A) was obtained from the controls (white bars) and ob/ob (black bars) mice, prior to the RCT procedure and used at 2.0% concentration on a set of cells expressed ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-BI. The cells were prelabelled with [3H]-cholesterol and incubated with the serum for 4 h before the amount of radiolabel was determined in the media by liquid scintillation counting. Percent cholesterol efflux was determined as concentration of label in the media as a function of total label in the cells. Cellular cholesterol efflux was also quantified using the apoB-depleted fraction of the serum (B) where serum was incubated with PEG (2:5), pelleted and then the supernatant used at 2.4% v/v. Freshly isolated adipose (C) and liver tissue (D) were cut into small pieces, cholesterol-loaded with [3H]-cholesterol and incubated for 4 h with cholesterol acceptors apoA-I and HDL or media (passive) to measure adipose and liver ex vivo efflux capacity. Freshly isolated adipose (E) and liver tissue (F) were also used to measure cholesterol uptake by measuring the amount of [3H]-cholesterol taken up over a 24 h period. Lipids were extracted from the tissue with isopropanol and [3H]-cholesterol quantified by liquid scintillation counting, which was then normalised to protein concentration in each well. RCT, reverse cholesterol transport; SR-BI, scavenger receptor class B type 1; ABCG1, ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 1; PEG, polyethylene glycol. *p<0.05; **p<0.002; ***p<0.00005;****p<0.003.