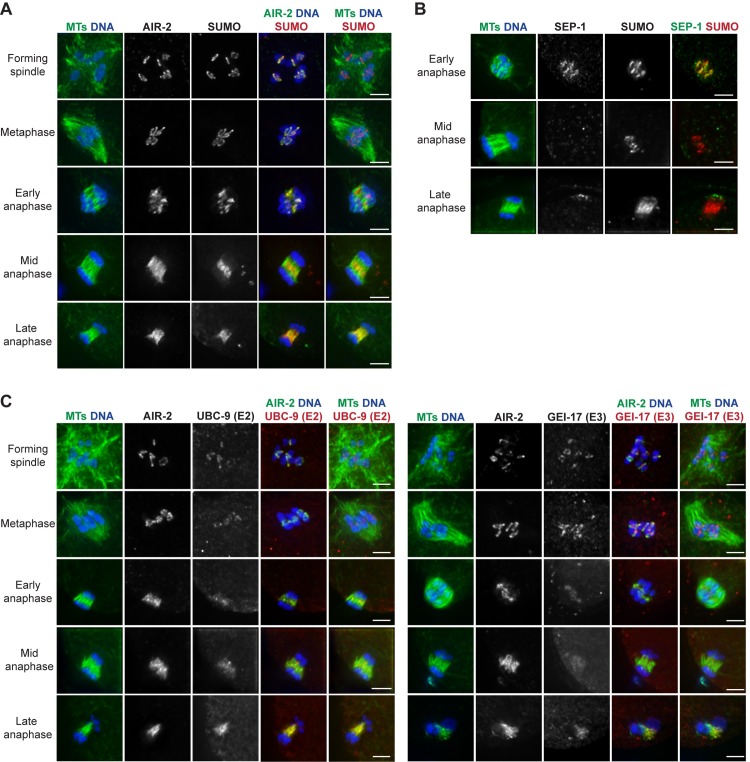
Fig 1. SUMO and SUMO E2/E3 enzymes leave the RCs during anaphase.
(A) Localization of SUMO (red) from spindle formation through late anaphase, compared to AIR-2 (green, column 4), DNA (blue), and tubulin (green, columns 1 and 5). SUMO becomes RC associated after NEBD, but leaves the RCs by late anaphase, relocalizing to the microtubules; SUMO remains RC-associated later into anaphase than AIR-2. (B) SUMO (red), compared to SEP-1 (green, column 4), DNA (blue), and tubulin (green, column 1) throughout anaphase. SUMO remains RC-associated after SEP-1 leaves. (C) Localization of UBC-9 (SUMO E2) (red, left panel) or GEI-17 (SUMO E3) (red, right panel) from spindle formation through late anaphase, compared to AIR-2 (green, column 4), DNA (blue), and tubulin (green, columns 1 and 5). UBC-9 and GEI-17 localize to the RCs during spindle assembly and then begin to leave these structures in early anaphase. Bar = 2.5μm.