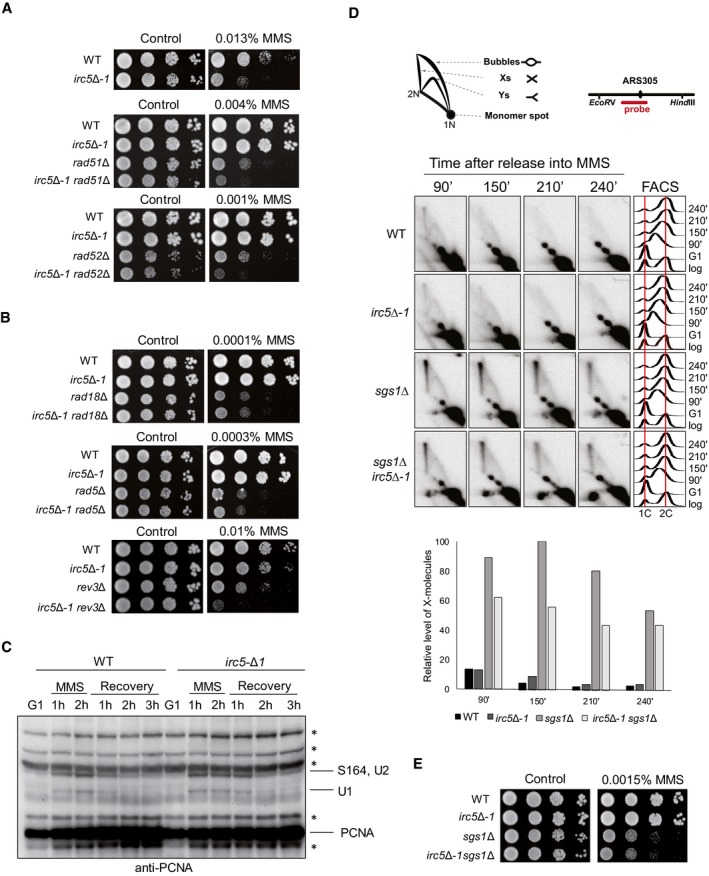
Genetic interactions between irc5‐Δ1 and HR mutants. Logarithmically growing cultures of wild‐type (W303‐1a), irc5‐Δ1 (IL012), rad51Δ (MC002), irc5‐Δ1 rad51Δ (TB046), rad52Δ (MC006), and irc5‐Δ1 rad52Δ (TB047) strains were 10‐fold serially diluted and plated onto YPD plates with or without MMS.
Disruption of IRC5 is epistatic to rad18Δ and rad5Δ mutations but not to rev3Δ. Logarithmically growing cultures of wild‐type (W303‐1a), irc5‐Δ1 (IL012), rad18Δ (MC019), irc5‐Δ1 rad18Δ (TB048), rad5Δ (MC018), irc5‐Δ1 rad5Δ (TB049), rev3Δ (MC021), and irc5‐Δ1 rev3Δ (TB050) strains were 10‐fold serially diluted and plated onto YPD plates with or without MMS.
The effect of irc5Δ‐1 mutation on PCNA posttranslational modifications. PCNA and its modified forms were detected using a polyclonal anti‐PCNA antibody. Asterisks indicate cross‐reacting bands.
Lack of Irc5 decreases formation of recombination intermediates during TS. Wild‐type (W303‐1a), irc5‐Δ1 (IL012), sgs1Δ (MC012), and irc5‐Δ1 sgs1Δ (TB051) cells were synchronized in G1 with alpha factor and released in media containing 0.03% MMS. The amount of replication intermediates at ARS305 was analyzed by 2D gel. Schematic representation of major 2D gel signals and DNA fragment analyzed is presented. Measurement of DNA content by FACS and X‐molecule quantification is displayed (n = 2).
irc5‐Δ1 is epistatic to sgs1Δ. Wild‐type (W303‐1a), irc5‐Δ1 (IL012), sgs1Δ (MC012), and irc5‐Δ1 sgs1Δ (TB051) strains were 10‐fold serially diluted and plated onto YPD plates with or without MMS.