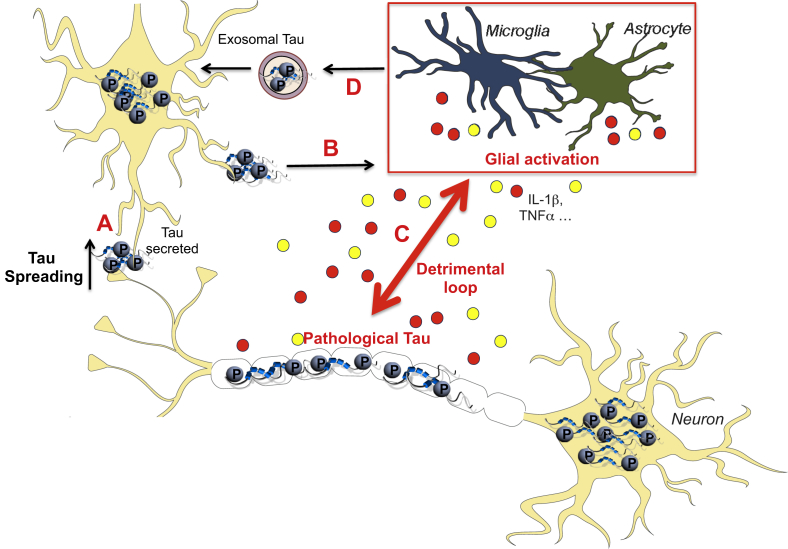
Fig. 1.
Innate Immune response and Tau pathology: a vicious circle. Hyperphosphorylated pathological Tau species can be secreted extracellularly, explaining the progressive spread of tauopathy (A). Therefore, it promotes microglial activation/reactive astrocytes which release cytokines or neurotoxic inflammatory molecules including IL1β or TNFα (B). By a modulation of Tau kinases (p38, cdk5…), glial activation enhances Tau pathology, self-perpetuating the detrimental circle (C). Also, microglia was observed to be involved in Tau propagation by releasing exosomal Tau once pathological Tau phagocytosed (D).