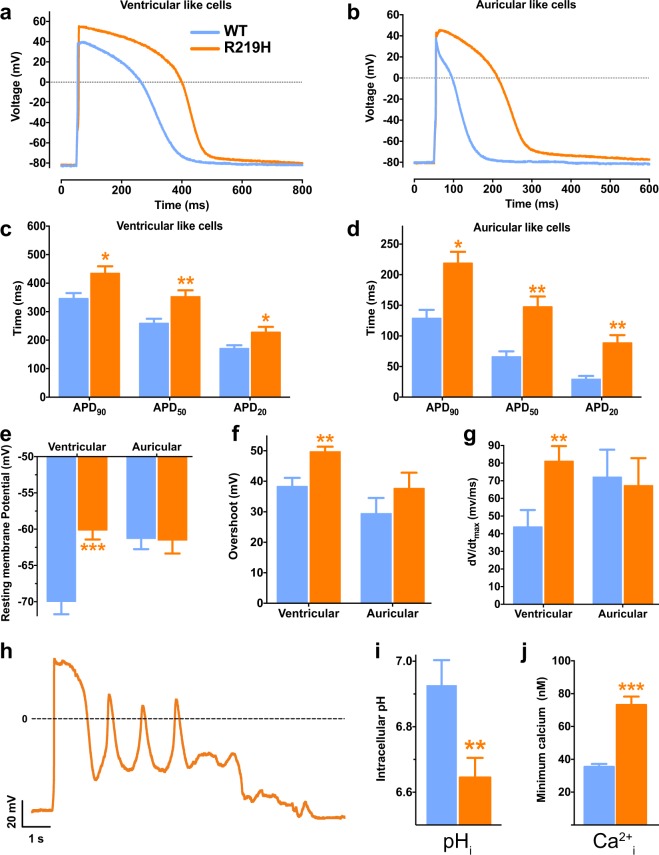
Figure 5.
Electrophysiological properties of WT and R219H hiPSC-CMs. The results for the WT hiPSC-CMs are indicated by blue symbols and those for the R219H hiPSC-CMs by orange symbols. APs were recorded for both WT and R219H hiPSC-CMs using the current clamp technique (whole cell configuration) where APs were elicited using 3-ms pulses at a frequency of 1 Hz. (a,b) Examples of raw traces of APs of ventricular-like and auricular-like cells recorded from WT and R219H hiPSC-CMs. (c,d) Ventricular-like (c) and auricular-like (d) hiPSC-CMs harboring the Nav1.5/R219H mutation exhibit a prolonged AP duration (APD). (e) The Nav1.5/R219H mutation caused a depolarization of the resting membrane potential (RMP) measured just after reaching the whole cell configuration. (f) The overshoot, defined as the maximum potential reached during the AP, is slightly higher for ventricular-like cells carrying the Nav1.5 R219H mutation. (g) dV/dt, defined as the maximal upstroke velocity of the AP, is also slightly higher for ventricular-like cells carrying the Nav1.5/R219H mutation. (h) Arrhythmic events (early after depolarizations, EADs) were recorded in gap-free mode (current clamp) for a ventricular-like R219H hiPSC-CM. (i) R219H hiPSC-CMs have an acidic intracellular pH as measured using the BCECF-AM fluorescent probe (n = 34 and 60 for the WT and R219H hiPSC-CMs, respectively). (j) Intracellular calcium levels were measured using the fura-2-AM ratiometric fluorescent probe (n = 106 and 78 for the WT and R219H hiPSC-CMs, respectively). The asterisks indicate differences between WT hiPSC-CMs (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). Detailed values and the number of experiments are reported in Table S3.