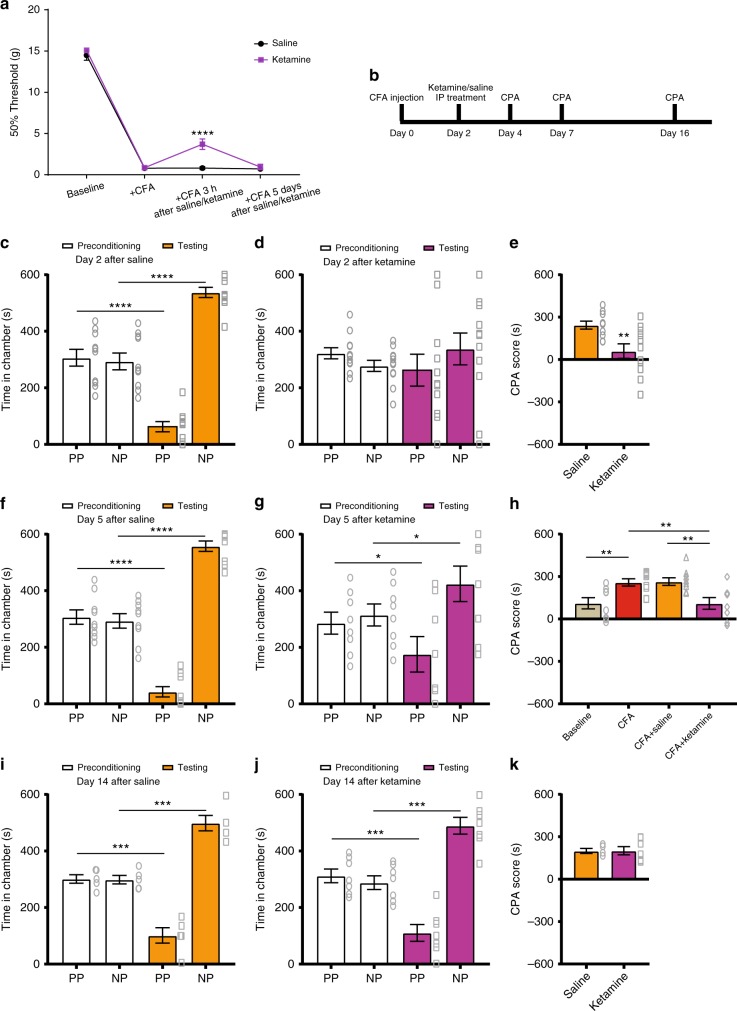
Fig. 2.
Ketamine provides long-lasting inhibition of affective symptoms of chronic pain. a A single sub-anesthetic dose of ketamine (10 mg kg−1) provides only transient relief of allodynia; n = 9–10; p < 0.0001. b Time course for CPA tests in ketamine-treated rats. c–e A single dose of ketamine inhibited the aversive response to acute pain in CFA-treated rats for at least 2 days. c CPA results 2 days after IP saline administration; n = 10; p < 0.0001, paired Student’s t-test. d CPA results 2 days after ketamine administration; n = 11; p = 0.2731. e CFA-treated rats demonstrate lower CPA scores 2 days after ketamine administration; n = 10–11; p = 0.0067, unpaired Student’s t-test. f–h A single dose of ketamine reduced the aversive response to acute pain in CFA-treated rats up to 5 days. f CPA results 5 days after saline administration; n = 9; p < 0.0001, paired Student’s t-test. g CPA results 5 days after ketamine administration; n = 8; p = 0.0333. h Ketamine restored the aversive response in chronic pain rats to baseline (−CFA) levels; n = 8–9; p = 0.0063, unpaired Student’s t-test. i–k The anti-aversive effect of ketamine in CFA-treated rats was eliminated 14 days after administration. i CPA results 14 days after saline administration; n = 5; p = 0.0003, paired Student’s t-test. j CPA results 14 days after ketamine administration; n = 7; p = 0.0005. k CPA scores for ketamine was similar to saline 14 days after administration; n = 5–7; p = 0.9665, unpaired Student’s t-test. Error bars represent S.E.M. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001