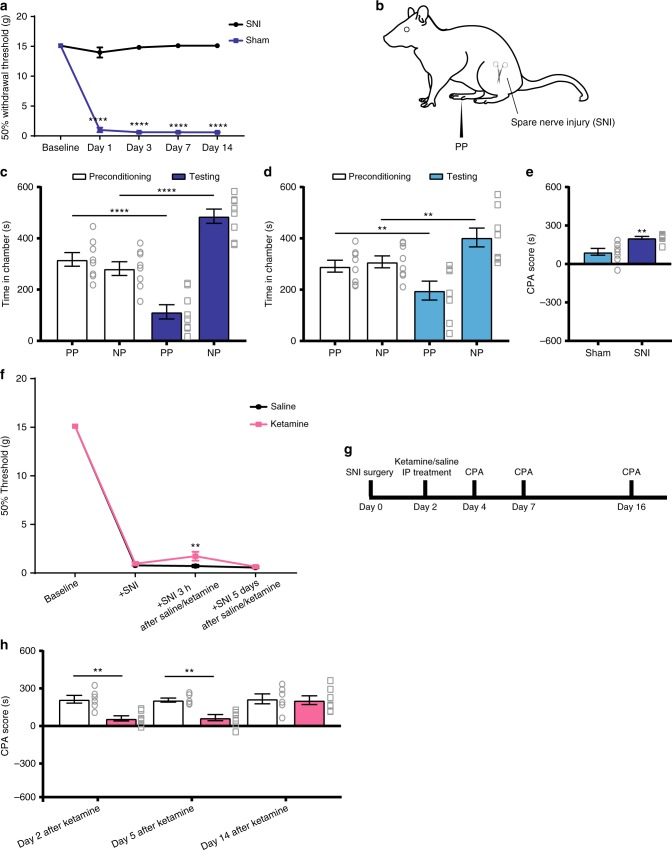
Fig. 4.
Ketamine reduced the enhancement in pain aversion in a chronic neuropathic pain model. a Rats developed persistent allodynia after SNI surgeries, n = 6; p < 0.0001. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures and post-hoc Bonferroni test. b Schematic of the CPA testing of the SNI-treated rats. c The aversive response to acute noxious stimulations was enhanced in SNI-treated rats; n = 8; p < 0.0001, paired Student’s t-test. d Rats displayed normal level of avoidance of the chamber associated with PP after sham surgery; n = 8; p = 0.0091. e SNI induced generalized enhancement of aversion to noxious stimulations, as demonstrated by the increased CPA score; n = 8; p = 0.0019, unpaired Student’s t-test. f A single sub-anesthetic dose of ketamine (10 mg kg−1) provided transient relief of mechanical allodynia in SNI-treated rats; n = 6–8; p < 0.0084. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures and post-hoc Bonferroni test. g Timeline for the CPA experiment in SNI-treated rats. h The anti-aversive effect of ketamine on SNI-treated rats was present 2 days (n = 6–7; p = 0.0021) and 5 days (p = 0.0048) but not 14 days (p > 0.9999) after its administration, two-way ANOVA with repeated measures and post-hoc Bonferroni tests. Error bars represent S.E.M. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001