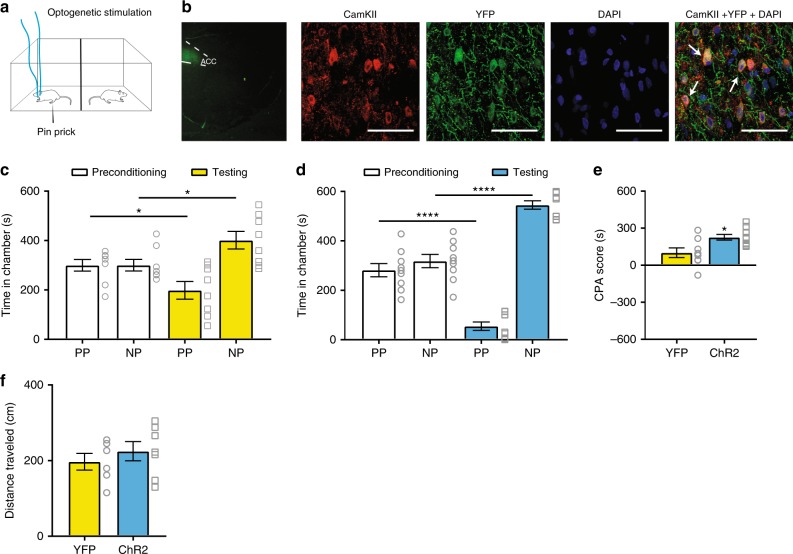
Fig. 6.
Ketamine inhibits ACC activities to reduce pain aversion. a Schematic of the CPA assay with optogenetic activation of the ACC in CFA-treated rats. Light stimulation was paired with PP in one chamber during the conditioning phase, and the other chamber was paired with NP. b Expression of YFP-ChR2 in the ACC. From left to right: low magnification (×20) view of ChR2-eYFP in the ACC; high-magnification (×100) view of CaMK II staining, YFP-ChR2 staining, DAPI staining, and Merged images. Arrows point to sample co-stained neurons. c, d ACC activation blocked the anti-aversive effects of ketamine in CFA-treated rats. c CPA test for YFP rats that received CFA and ketamine treatments; n = 8; p = 0.0381, paired Student’s t-test. d CPA test for ChR2 rats that received CFA and ketamine treatments; n = 9; p < 0.0001. e The anti-aversive effect of ketamine in CFA rats was eliminated by the activation of ACC, as shown by the increased CPA score in the ChR2 group; n = 8–9; p = 0.0133, unpaired Student’s t-test. f Activation of the ACC did not alter locomotion; n = 7; p = 0.4348, unpaired Student’s t-test. Error bars represent S.E.M. Scale bar equals 50 μm in b. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001