Fig. 3.
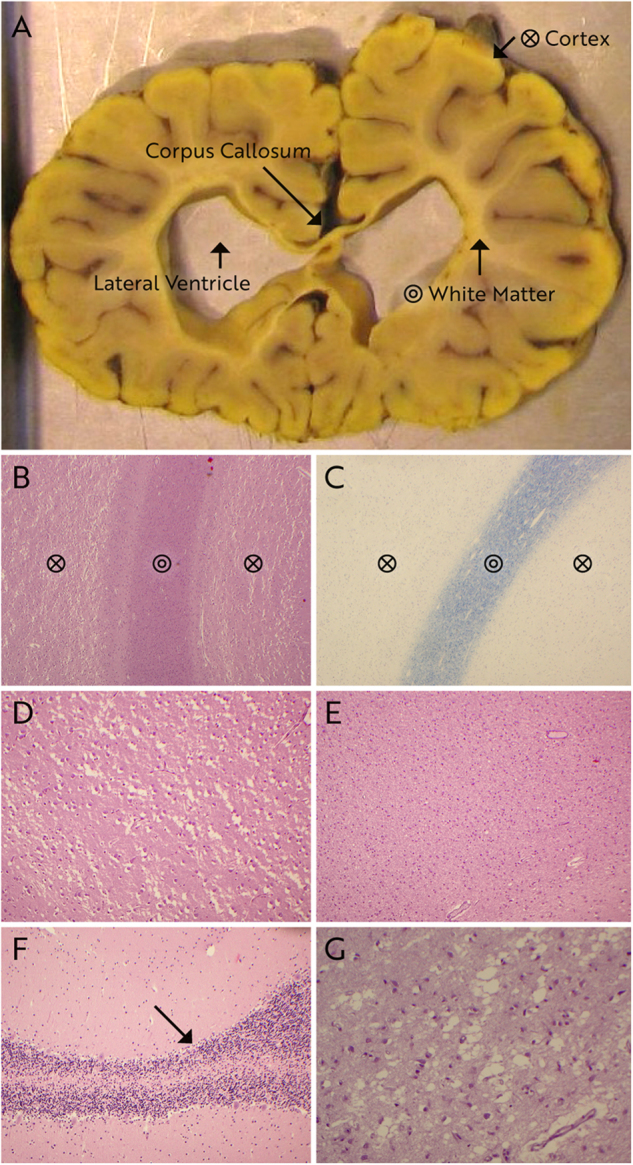
Macroscopic (a) and histopathological (b–g) examination of brains of case 6 at 10 months of age (f) and case 7 at 11 months of age (a–e, g). Staining is hematoxylin & eosin (b; d–g) and Klüver–Barrera (c). White matter volume is severely reduced leading to ventriculomegaly of lateral ventricles and extreme thinning of corpus callosum (a). The yellow discoloration of the brain is due to fixation in picrid acid. Histologically, cortex is showing marked vacuolization and severe neuronal loss (b, d), substantially reduced volume of the white matter (b), but normal myelin content in Klüver–Barrera stain (c), exemplified in the frontal lobe. A profound gliosis in the white matter of the frontal lobe is seen (e). These findings were verified in the other cortical areas of both patients (not shown). The cerebellum displayed mild loss of purkinje cells in patient 6 (f) and in hippocampus severe neuronal loss in cornu ammonis area 1 and area 2 in patient 7 (g)
