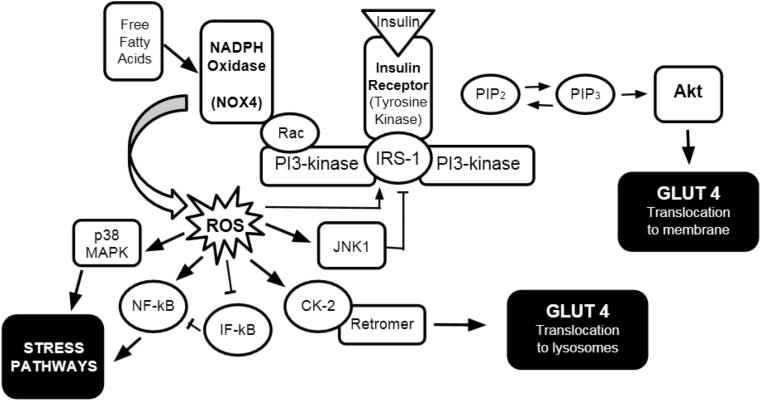
Fig. 1.
Insulin receptor signaling pathway including ROS influence. The normal pathway begins with insulin binding insulin tyrosine kinase receptor. The insulin receptor phosphorylates insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) [10] which in turn phosphorylates PI3-kinase. PI3-kinase then phosphorylates PIP2 which then activates Akt [11], eventually leading to glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation to the plasma membrane of skeletal muscle cells and adipocytes, thus allowing the cell to absorb extracellular glucose, lowering interstitial glucose levels and thus plasma glucose concentration. Abbreviations used: PIP2 and PIP3: phosphatidylinositol species; Rac: Rac GTPase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; JNK1: c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1; CK-2: Casein kinase 2; NF-kB: nuclear factor kB; IF-kB: Inhibitory factor kB; p38 MAPK: p38 mitogen activated protein kinase; Akt: protein kinase B.