Figure 4. RNA splicing perturbation by pharmacologic compounds induce R loop-associated ATR-mediated RPA32 phosphorylation.
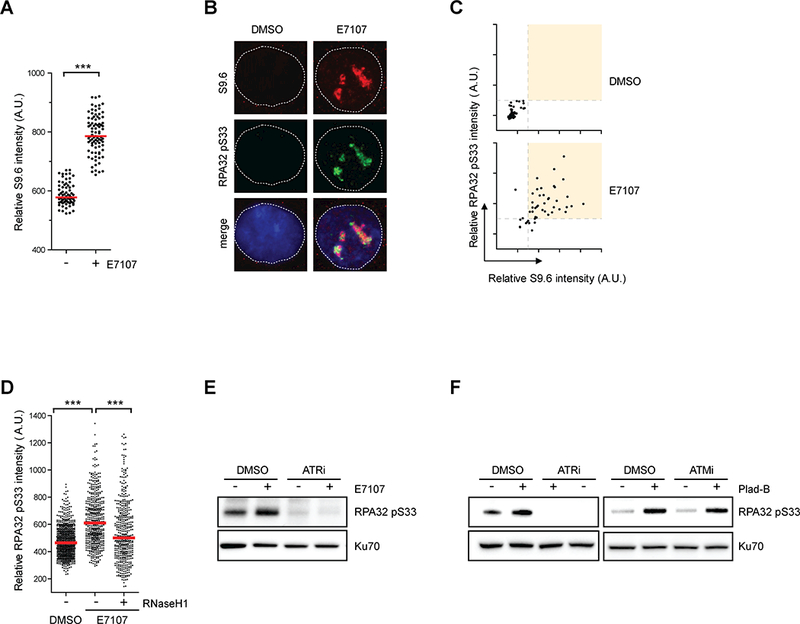
(A) HeLa cells were treated with DMSO or E7107 (1 nM) for 24h. Individual cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence using the S9.6 antibody. Intensities of S9.6 staining in individual cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence (n>70). Red bars represent the median S9.6 intensities of the indicated cell populations. ***, p≤0.001. (B-C) HeLa cells were treated with DMSO or E7107 (2 nM) for 24h. In B, representative images individual cells stained with S9.6 and p-RPA. In C, intensities of S9.6 and p-RPA staining of individual cells were plotted in 2D. (D) HeLa cells inducibly expressing RNaseH1 were treated with DMSO or E7107 (1 nM) for 24h. RNaseH1 expression was induced by addition of doxycycline as indicated. Intensities of RPA32 pS33 staining in individual cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence (n>460). Red bars represent the median RPA32 pS33 intensities of the indicated cell populations. ***, p≤0.001. (E) HeLa cells were treated with DMSO or E7107 (2 nM) for 24h, followed by ATRi treatment (10 μM, 1h). Indicated proteins were analyzed by western blot. (F) HeLa cells were either treated with DMSO or 1 nM Plad-B. After 24h treatment, ATR or ATM inhibitors (10 μM) were added for 1h. Levels of indicated proteins were analyzed by western blot.
