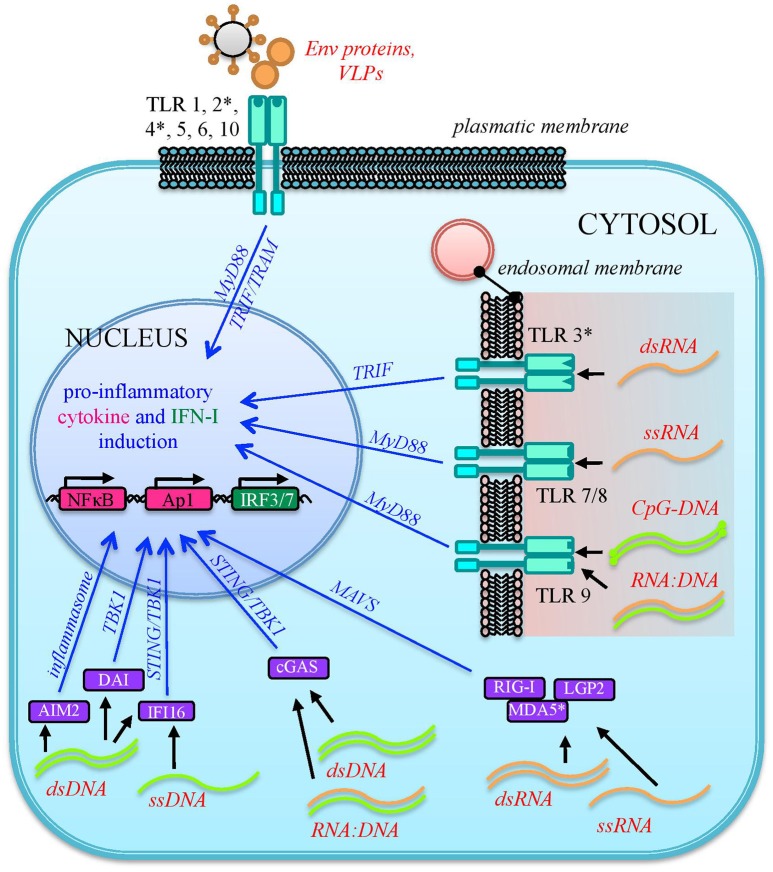
Figure 3.
Sensing of HERV molecules by innate immunity PRRs. Different HERV proteins and nucleic acids (overall indicated in red) can theoretically be detected as PAMPs or DAMPs by cellular sensors localized at the plasmatic or endosomal membranes (transmembrane PRRs or Toll Like Receptors, cyano) or present as soluble factors in the cytosol (cytosolic PRRs, violet). The sensing of these viral molecules by both kind of PRRs triggers a signaling cascade (blue arrows) that leads to the nuclear activation of immune genes encoding for pro-inflammatory effectors, represented by cytokines and type I IFN. The individual PRRs for which a direct interaction with HERV molecules has been reported are marked with an asterisk.