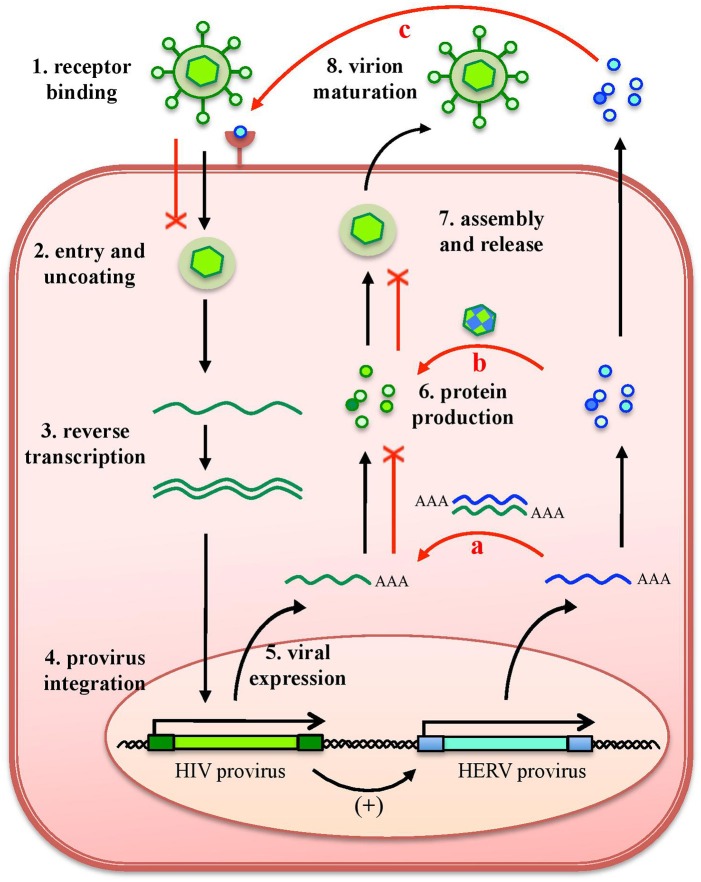
Figure 4.
Protective effects exerted by HERVs against exogenous infections. The effects of HERV expression in the impairment of exogenous viruses (red lines) are represented in relation to HIV infection. The various steps of HIV replication are also schematized. Even if HERV expression could theoretically affect any of them, the major implications regard (a) the expression of HERV mRNAs, that can interact by complementarity with HIV RNA, could form dsRNA that is detected as a PAMP by cellular innate immunity sensors; (b) the complementation of HIV structural components with HERV proteins, possibly affecting HIV particles' assembly and release; and (c) the binding of HERV proteins or pseudoparticles to the same cellular receptor, preventing HIV binding and entry. Of note, these effects can be eventually sustained also by the possible upregulation of HERV expression by HIV infection.