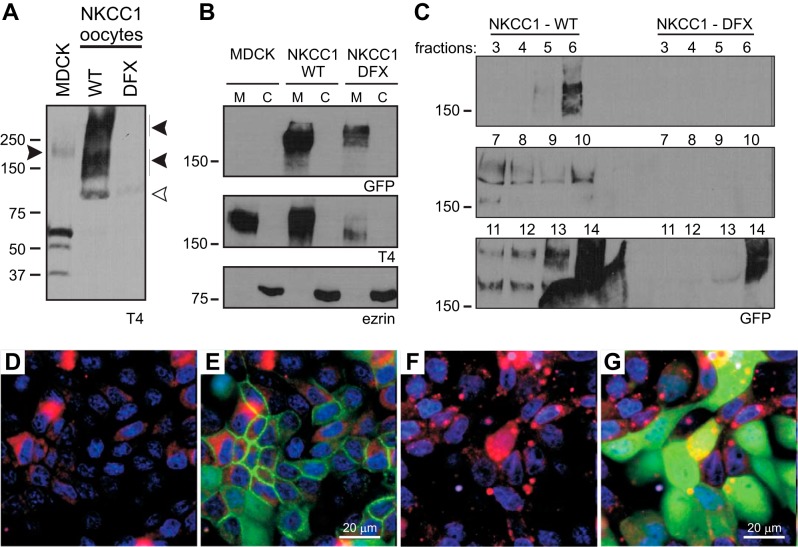
Fig. 3.
NKCC1-DFX is associated with membranes and trafficked out the ER. A: oocytes were injected with NKCC1-WT or NKCC1-DFX cRNA, lysed, and analyzed by Western blotting. T4 antibody, which targets the carboxyl-terminal domain of NKCC1, does not recognize the NKCC1-DFX mutant. Solid arrows, NKCC1 signal; open arrow, unspecific signal. B: subcellular fractionation of MDCK cells stably transfected with NKCC1-WT and NKCC1-DFX followed by immunoblotting of each fraction with GFP, T4, and ezrin antibodies. C: whole cell lysates of MDCK transfected with MDCK-WT and MDCK-DFX were fractionated on a discontinuous sucrose gradient. Aliquots (40 μl) of fractions (0.8 ml) collected from the top were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting. D–G: MDCK-WT (D and E) and MDCK-DFX (F and G) were cultured in MatTek Glass Bottom Microwell dishes. Cells were stained with PureBlu Hoechst 33342 and ER-Tracker Red and imaged live on the Zeiss LSM 880 confocal microscope. Bars, 20 μm. C, cytosolic compartment; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GFP, green fluorescent protein; M, membrane compartment; MDCK, Madin-Darby canine kidney; NKCC1, Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter-1; WT, wild type.