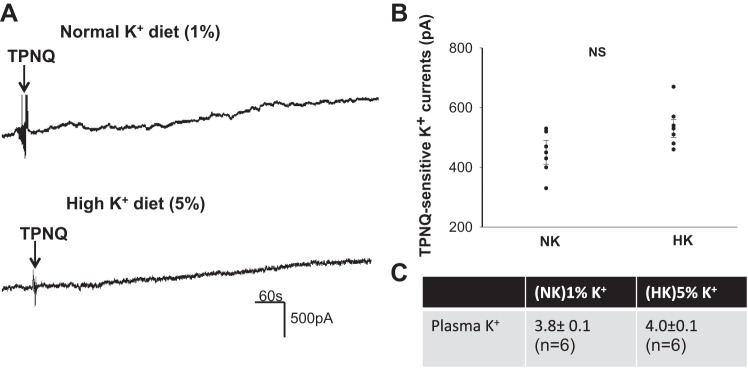
Fig. 5.
Deletion of kidney-specific-with-no-lysine kinase (KS-WNK1) abolishes the effect of high potassium (HK) on ROMK in late distal convoluted tubule (DCT2)/connecting tubule (CNT). A: whole cell recording shows tertiapin-Q (TPNQ)-sensitive K+ currents at −40 mV in DCT2/CNT of kidney-specific-with-no-lysine kinase-null (KS-WNK1−/−) mice on normal K+ (NK) and HK. Arrows indicate the addition of 400 nM TPNQ to the bath. B: scatterplot summarizes the experiments in which TPNQ-sensitive K+ currents were measured at −40 mV with whole cell recording. Results were obtained from six experiments (tubules). C: table shows plasma K+ concentration of KS-WNK1−/− mice on NK and HK diets for 7 days (n = 6 mice).