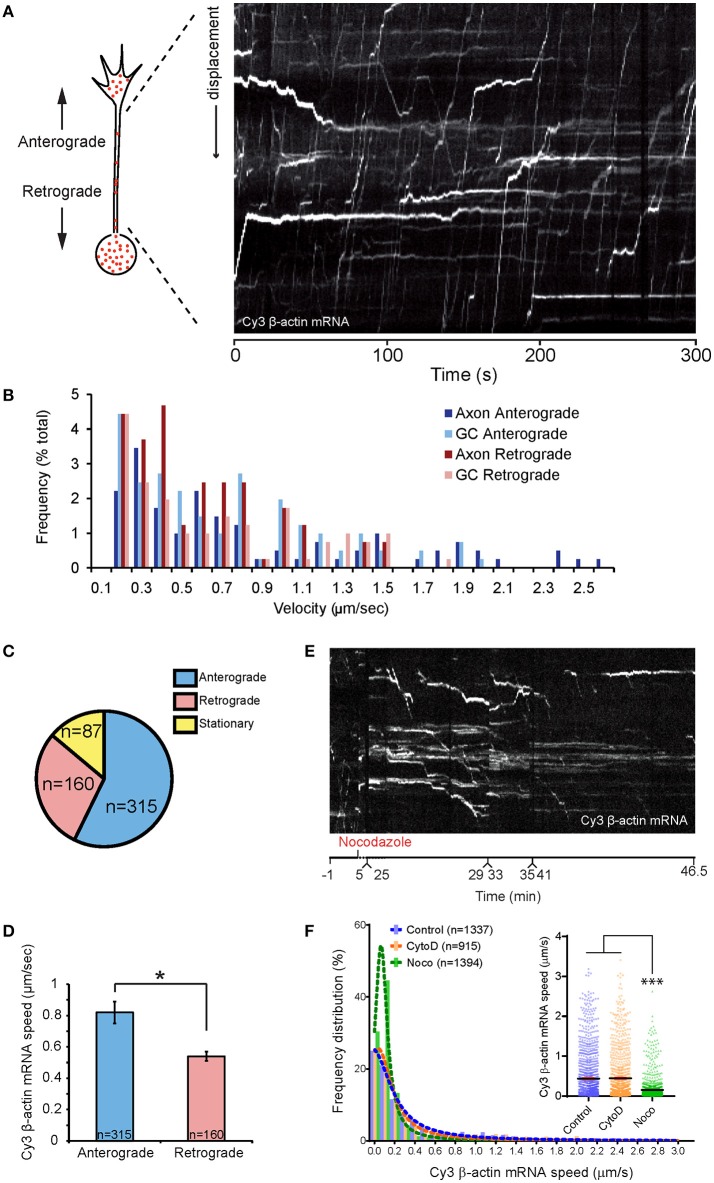
Figure 2.
Dynamics of β-actin mRNA granules in axons. (A) An example of kymographs generated along axon shaft for kinetics analysis. (B) Population distribution of β-actin mRNA granule speeds for anterograde- and retrograde-moving granules in axon and growth cone. β-actin mRNA granule speeds showed biphasic distribution. One peak consisted of stationary and slow diffusive motion with speed < 0.5 μm/s. The more motile population showed a bell-shaped distribution. High speed (>2 μm/s) was observed for anterograde-moving granules along the axon shaft. (C) Proportion of anterograde-moving, retrograde-moving, and stationary β-actin mRNA granules in axons (n = 562 granules). (D) Anterograde-moving granules showed higher average speed than retrograde-moving granules. Nocodazole treatment greatly reduced kymographic tracks of fast-moving mRNA granules within 30 min, leaving mainly horizontal tracks from stationary mRNA granules. (F) Average instantaneous speed of all β-actin mRNA granules obtained from automated tracking is presented. The speed reduced to below 0.15 μm/sec upon 35-min nocodazole (Noco) treatment, but was unchanged upon 20-min cytochalasin D (CytoD) treatment. [F(2, 3643) = 146, p < 0.0001]. Error bars represent SEM. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons test for F).