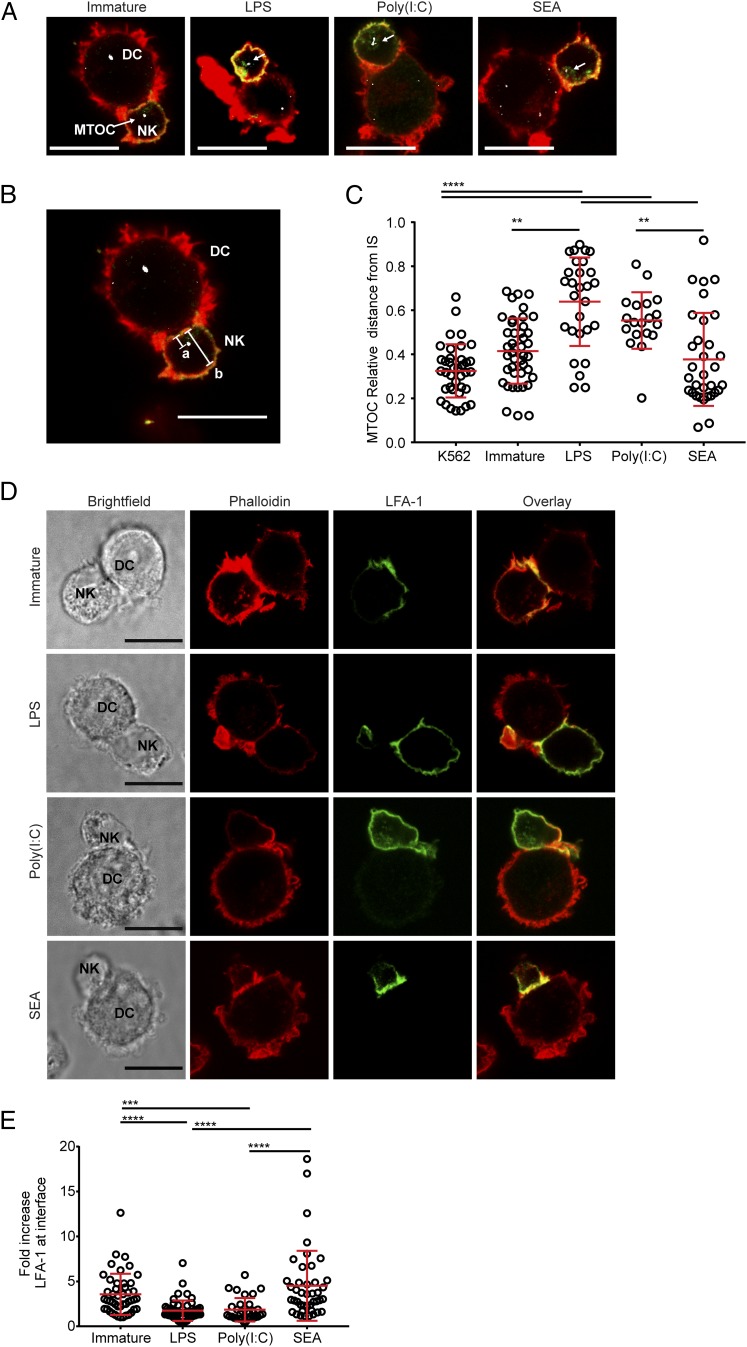
FIGURE 3.
NK cells show MTOC and LFA-1 reorganization in conjugates with DCs treated with SEA. (A) Panels show autologous NK cells conjugated with immature DCs (left) or DCs treated for 24 h with LPS, poly(I:C), or SEA, overlays of cells stained with phalloidin (red), anti-NKp30 mAb (green), and antipericentrin polyclonal Ab (white). Representative data from >150 images taken over three independent experiments; scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Example of MTOC distance measurement with image from (A). Distance from MTOC to cell–cell interface (line labeled as a) is divided by the diameter of the NK cell (line labeled as b). (C) Relative distance of the NK cell MTOC from immune synapse in conjugates with K562 target cells, immature DCs, or DCs treated for 24 h with LPS, poly(I:C), or SEA. (D) Panels show images of autologous NK cells conjugated with immature DCs or DCs treated for 24 h with LPS, poly(I:C), or SEA stained with phalloidin (second column, red) and anti–LFA-1 mAb (third column, green). A brightfield image (left) and overlay of the two channels (right, yellow shows colocalization) are also shown. Images representative of >150 images taken across three independent experiments; scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Fold increase in fluorescence intensity of staining with anti–LFA-1 mAb at the cell interface, compared with the back of the NK cell, in conjugates with immature DCs and DCs treated for 24 h with LPS, poly(I:C), or SEA. In all plots, circles represent data points from individual cell contacts pooled from three independent donors; lines show mean (±SD). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn multiple comparisons.