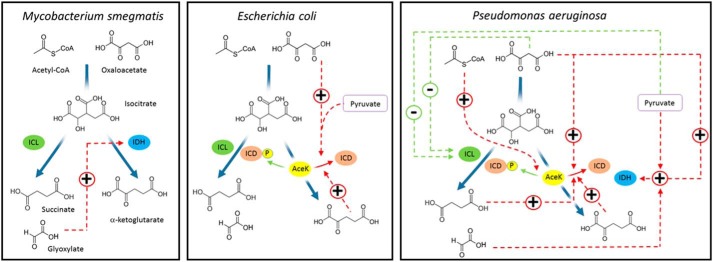
Figure 6.
Comparison of TGB regulatory mechanisms in M. smegmatis, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa. Interactions that stimulate the target enzyme are shown in red, whereas interactions that inhibit the target enzyme are shown in green. For simplicity, we have only shown the regulatory interactions of the molecules depicted in the figure. A more comprehensive schematic of the regulatory interactions established for P. aeruginosa is shown in Fig. S12. Note that for simplicity, the pathway from acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to isocitrate is depicted as a single step in the figure, whereas this conversion is catalyzed by the sequential action of citrate synthase and aconitase in the cell.