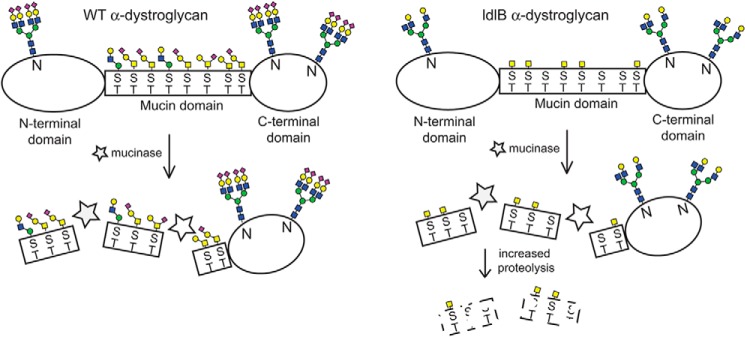
Figure 1.
Domain structure of α-dystroglycan and proposed role of mucin-type glycans in protein stability. The mucin region of α-dystroglycan bears both GalNAc- and mannose-initiated glycans flanked by N- and C-terminal domains that contain N-glycans. ManNAz is incorporated into sialic acid on both N- and O-glycans, whereas GalNAz is mainly incorporated into GalNAc-containing O-glycans. The cleavage of α-dystroglycan by bacterial mucinases occurs in both WT and ldlB CHO cells despite major effects on the mucin-type glycans of this glycoprotein. The susceptibility of the resulting fragments toward other bacterial proteases, however, is influenced by the extent of mucin-type glycosylation on the fragments.