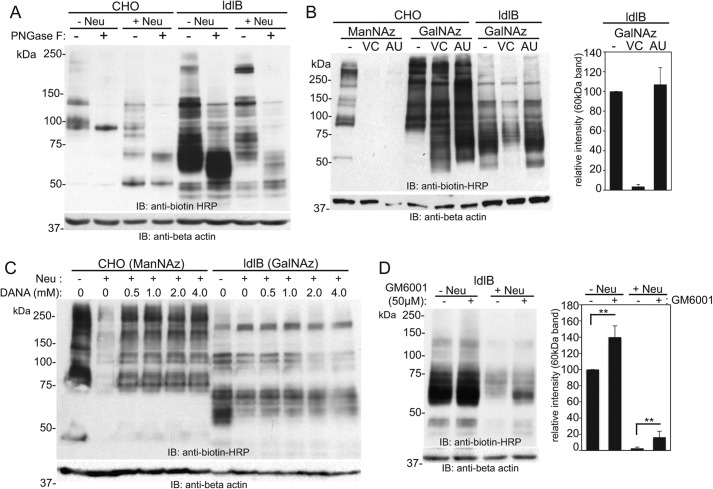
Figure 3.
The major GalNAz-labeled 60-kDa band in ldlB cells is an O-glycosylated protein susceptible to V. cholerae proteases that co-purify with its neuraminidase. A, WT CHO and ldlB cells were labeled with Ac4GalNAz, treated with or without V. cholerae neuraminidase, and then reacted with S-DIBO-biotin. The resulting cells were lysed, and the lysates from each condition were treated with or without PNGase F following by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting analysis using an anti-biotin–HRP antibody. A representative blot is depicted from three separate analyses. B, WT CHO and ldlB cells were labeled with ManNAz or GalNAz, and the labeled cells were treated with either V. cholerae or A. ureafaciens neuraminidase, followed by S-DIBO-biotin reaction and Western blotting using anti-biotin–HRP. Note that both neuraminidases can cleave sialic acids, but only the V. cholerae neuraminidase removes the 60-kDa band. The relative intensity of this band was quantified (average ± standard error of the mean; n = 2). C, ManNAz-labeled WT CHO and GalNAz-labeled ldlB cells were treated with V. cholerae neuraminidase in the presence of increasing amounts of the general neuraminidase inhibitor DANA. Following S-DIBO-biotin reaction on whole cells, resulting lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-biotin–HRP. A representative blot from two separate experiments is shown. D, GalNAz-labeled ldlB cells were treated with or without V. cholerae neuraminidase in the presence or absence of 50 μm GM6001, a general metalloproteinase inhibitor. Following S-DIBO-biotin reaction, the resulting cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with anti-biotin–HRP. Quantification of the intensity of the 60-kDa band relative to untreated ldlB cells was performed from three independent experiments (errors bars represent standard error). IB, immunoblot.