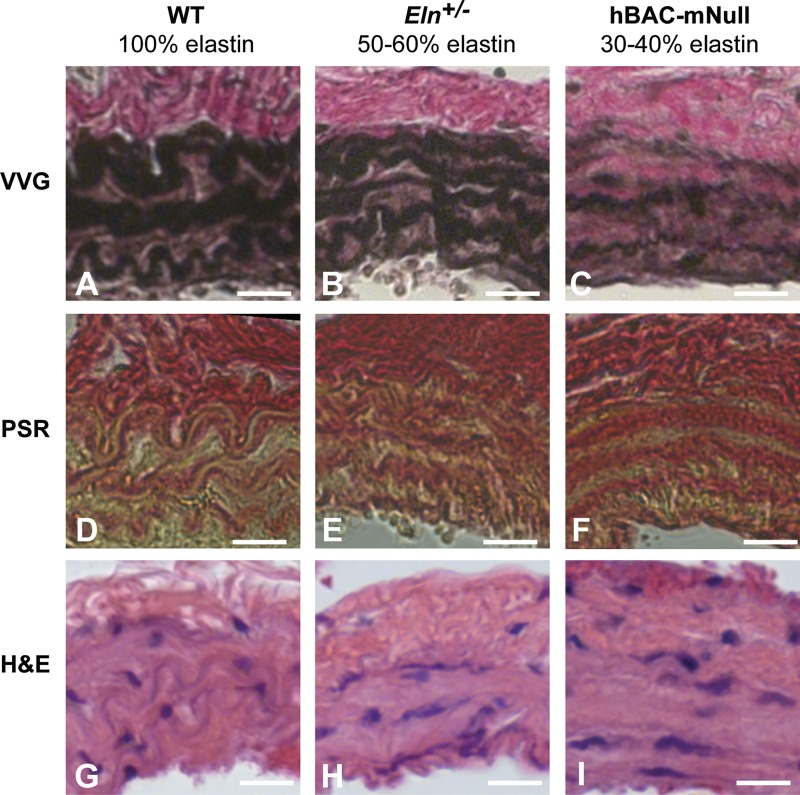
Fig. 5.
Effects of elastin amounts on arterial wall structure and composition. A−I: Histological sections (93) of the left common carotid artery from wild-type (WT) mice with 100% elastin (A, D, and G), Eln+/− mice with 50–60% elastin (B, E, and H), and hBAC-mNull mice with 30–40% elastin (C, F, and I). A–C: Verhoeff-Van Gieson (VVG)-stained sections show black elastic laminae, brown muscle tissue, and pink collagen. The elastic laminae are thinner, more numerous, and have more diffuse staining as elastin amounts decrease. D−F: picrosirius red (PSR)-stained sections show collagen fibers in red and other material in yellow. In WT arteries, red collagen clearly outlines the yellow elastic laminae. In Eln+/− and hBAC-mNull arteries, the collagen staining overlaps with the elastic laminae. G−I: hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained sections show cell nuclei in purple and other material in pink. Scale bars = 20 μm.