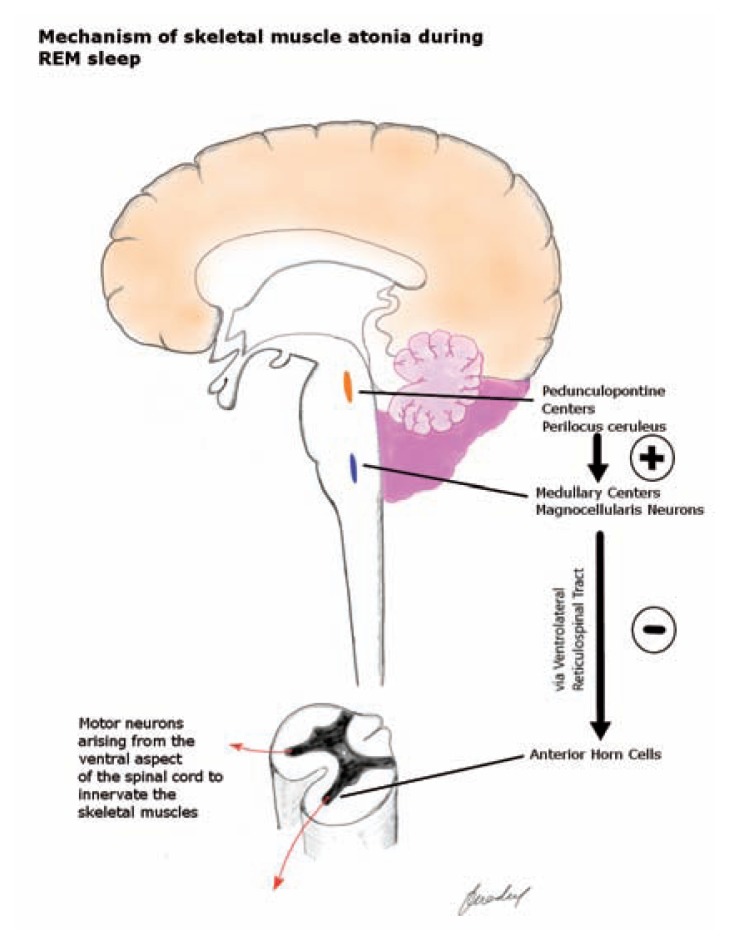
Figure 2.
The Perilocus Coeruleus region of the pons exerts an excitatory influence on the medullary ‘Magnocellularis’ neurons via lateral tegmentoreticular tract. These neurons project on to the spinal alpha motor neurons in the ventral horn via ventrolateral reticulospinal tract and cause hyperpolarization. This results in reduced muscle tone during the REM sleep. In RBD, the brainstem mechanisms that generate REM sleep related muscle atonia are disrupted.