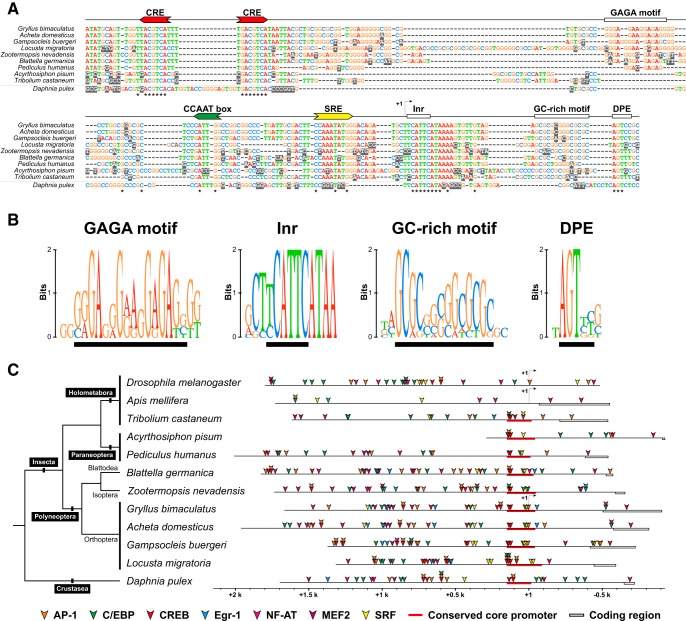
Figure 3.
Gene regulatory regions of the insect/crustacean egr-B homologs. A, Putative core promoter regions of basal insect and crustacean egr-B homologs share a high-level sequence similarity. The upstream sequences of insect/crustacean egr-B homologs are aligned with the core promoter region of Gryllus egr-B. The conserved bases are marked with asterisks under the alignment. Cis-regulatory elements and sequence motifs that are conserved are indicated above the alignment. CRE, cAMP-responsive element; SRE, serum response element; Inr, initiator element; DPE, downstream promoter element. B, Sequence logo representation of the conserved motifs in the core promoter region of insect egr-B homologs. The sequence logo of the GAGA motif was generated by multiple alignment of the upstream sequences of polyneopteran egr-B homologs. The other sequence logos were generated by multiple alignment of the upstream sequences of insect egr-B homologs. The positions of conserved motifs are indicated by black bars under the logo. C, Schematic representation of the gene regulatory regions of insect/crustacean egr-B homologs. The genomic regions were aligned to the position of the +1 site of Gryllus egr-B or the 5′-end of the putative core promoter region. The red bars indicate genomic regions aligned in Fig. 3A. Positions of transcription factor binding sites predicted using the LASAGNA-Search 2.0 program (score >8.0) are indicated by arrowheads. The phylogenetic relationship of insect/crustacean species is indicated as a phylogram tree. AP-1, activator protein 1; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; C/EBP, CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein; MEF2, myocyte enhancer factor 2; NF-AT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells; SRF, serum response factor. See Table 2 for the details of genomic sequences used for promoter analysis. See Fig. 3-1 and Table 3-1 for the structural conservations of the transcription factors used for the binding site prediction.