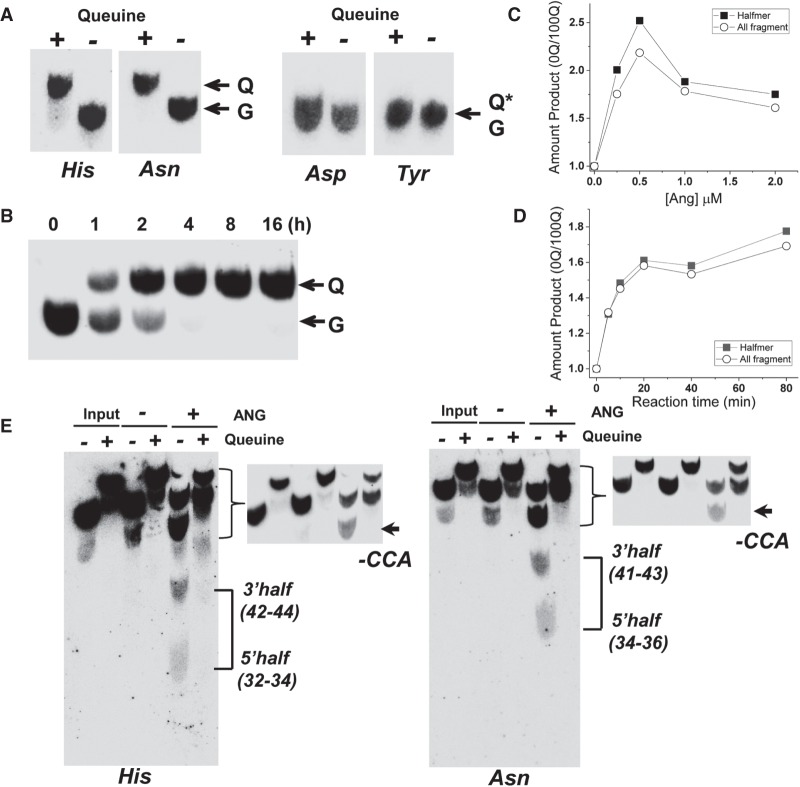
FIGURE 1.
Q modification inhibits angiogenin cleavage in vitro. (A) Northern blot analysis of total RNAs isolated from 0Q, 100Q HEK293T cells probed against tRNAHis, tRNAAsn, tRNAAsp, and tRNATyr separated by APB-containing gels. Q, Q*, and G indicate tRNA with Q34, glycosylated Q34 and G34, respectively. (B) Appearance of Q modification for tRNAAsn starting from the addition of queuine to HEK293T 0Q cells. Q and G indicate tRNA with Q34 and G34, respectively. (C,D) Comparative amount of angiogenin cleavage products upon varying the angiogenin concentration (C) or reaction time (D) of total tRNA isolated from 0Q and 100Q HEK293T cells. tRNAs were 5′ 32P-labeled, so the products can be identified by size. Comparison includes either only tRNA halfmer products corresponding to cleavage in the anticodon loop or all fragments derived from cleavage anywhere in the tRNA body. (E) Northern blot analysis of tRNA cleavage by angiogenin separated by APB-containing gels using the tRNAHis probe on the left and tRNAAsn probe on the right. Northern blot detected both 5′ and 3′ cleavage product in the anticodon loop; these halfmers in the 0Q sample are indicated by connecting lines on the right, and the size of the products is shown in parentheses. The product near the full-length likely corresponds to angiogenin cleavage of the 3′CCA tail; these are indicated by an arrow and -CCA on the right. A high contrast image of this portion is also shown for better visualization. Quantitation of these products is shown in Supplemental Table S1. Q-containing tRNA fragments are shifted in the 100Q sample.