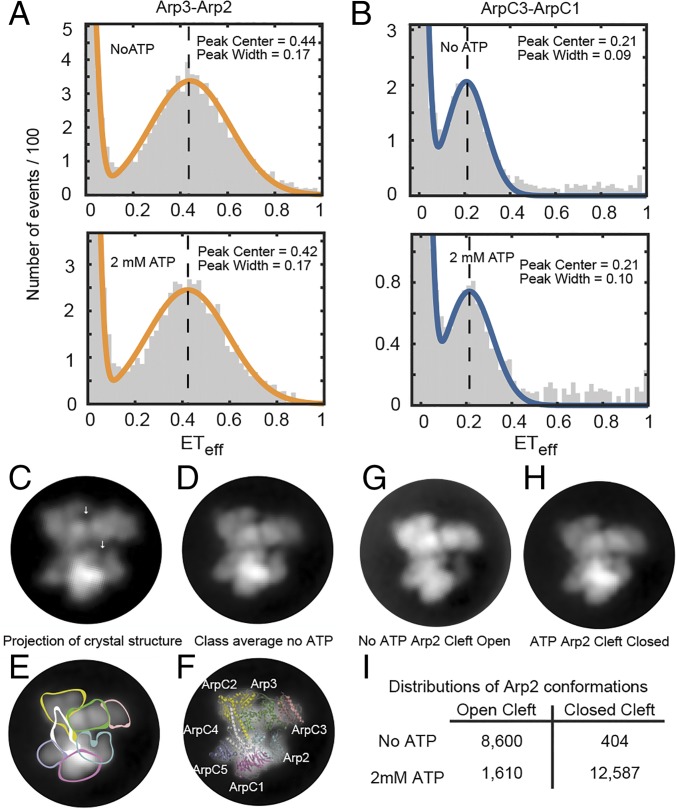
Fig. 4.
Effect of ATP on the conformation of Arp2/3 complex. (A and B) smFRET experiments (Upper) without ATP and (Lower) with 2 mM ATP. Conditions: 75 pM Arp2/3 complex and 40 nM unlabeled Arp2/3 complex in KMET buffer (50 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM DTT, and 10 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 7.0). Vertical dashed lines indicate the mean of the ETeff peaks without ATP as a visual guide. (A) Arp2cys-Arp3cys construct. (B) ArpC1cys-ArpC3cys construct. (C) Low-resolution (20 Å) 2D projection of the crystal structure of bovine Arp2/3 complex with Ca-ATP in the same orientation as the negative stain class averages. The model was made from PDB ID code 4JD2 with mouse GMF deleted. White arrows indicate the nucleotide-binding clefts of Arp2 (lower) and Arp3 (upper). (D–G) Transmission EM of negatively stained Arp2/3 complex without ATP. Virtually all of the particles had the same orientation. After correction for drift, particles were classified and class averages computed. (D) A dominant class average of the projection structure of Arp2/3 complex without ATP computed from 2,066 particles. (E) Subunits are outlined on the class average. (F) A ribbon diagram of the crystal structure of inactive Arp2/3 complex is superimposed on the class average. (G) Dominant class average without ATP (1,636 particles) with the nucleotide-binding cleft of Arp2 open. (H) Dominant class average with ATP with the nucleotide-binding cleft of Arp2 closed. (I) Numbers of particles in two class averages.