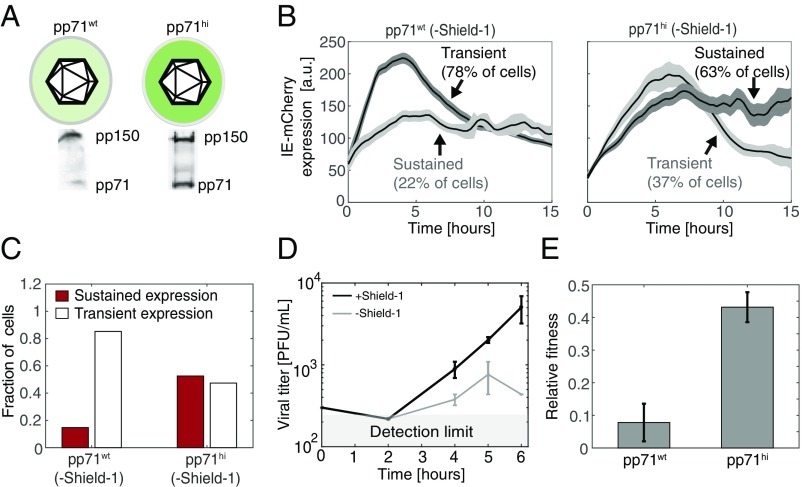
Fig. 4.
Increased pp71 abundance partially rescues expression and fitness of attenuated feedback virus. (A) Western blot analysis of pp71 in viral particles packaged on cells overexpressing pp71 (IE1-CMDR-pp71hi) or on nonoverexpressing cells (IE1-CMDR-pp71wt). (B) Representative time-lapse microscopy traces of IE-mCherry expression in cells infected with IE1-CMDR-pp71hi or IE1-CMDR-pp71wt. Cells were cultured without Shield-1 (attenuated feedback) and classified as sustained or transient based on expression kinetics as defined above. Bold line denotes mean mCherry signal of sustained or transient cells; shaded area denotes SE. Cell trajectories were digitally synchronized to the first detection of mCherry signal. (C) The fraction of cells with sustained IE-mCherry expression (STI > 0.5) after infection with IE1-CMDR-pp71hi virus (116 cells) or IE1-CMDR-pp71wt virus (243 cells). Cells were cultured without Shield-1 (attenuated feedback). P < 0.001 was calculated using a Fisher exact test. (D) High pp71 can partially compensate the fitness lost when feedback is attenuated. Viral titers from cells infected with IE1-CMDR-pp71hi virus ± Sheild-1. Cells were infected in medium with 1 μM Shield-1 (black, wild-type feedback) or without Shield-1 (gray, attenuated feedback), virus was harvested at indicated times after infection, and titers were measured in medium supplemented with 1 μM Shield-1. Compare with Fig. 3A. (E) High pp71 partially compensates for fitness lost when feedback is attenuated. Relative single-round fitness (titer at day 4) for either IE1-CMDR-pp71wt (Left) and IE1-CMDR-pp71hi (Right) when feedback is attenuated (−Shield-1) normalized to viral titer for corresponding wild-type feedback (+Shield-1) case (P = 0.041, two-tailed t test).