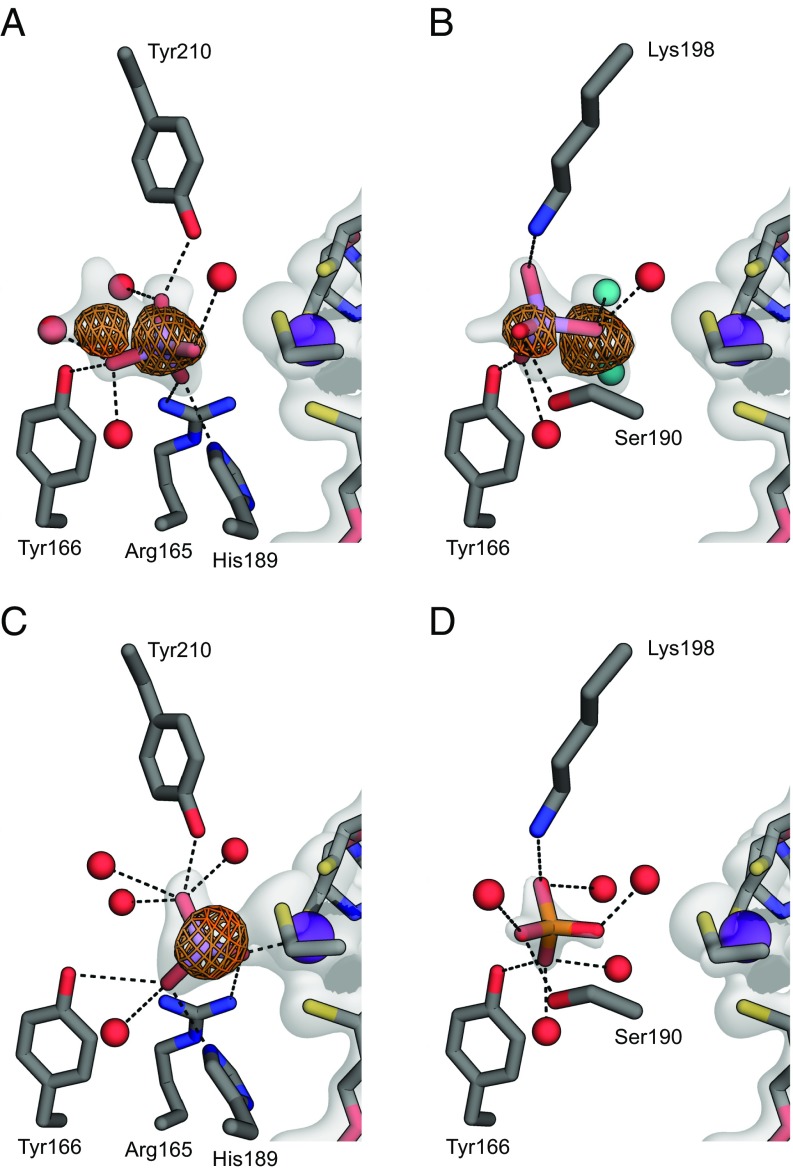
Fig. 2.
Close-up view of the arsenate-binding site in ArrA (C in gray, N in blue, O in red, S in yellow, P in orange, Mo in purple, and As in light purple). The 2mFo − Fc map around the relevant portions is shown as a white surface contoured to 1.5σ. For clarity, the map is shown only around ligands, the Mo-bisPGD cofactor, and the Mo-coordinating cysteine. The anomalous map collected at a wavelength of 1 Å is shown around arsenic atoms contoured to 6σ. Dashed lines indicate possible hydrogen bonds or coordination to the Mo atom. (A) Arsenate bound in the conformation nearest the Mo atom. (B) Arsenate bound in a second conformation farther from the Mo atom. The two water molecules in teal substitute for oxygen atoms from the first conformation shown in A. (C) Arsenite bound and coordinated to the Mo atom. (D) Phosphate bound to the active site in a conformation resembling the arsenate conformation from B.