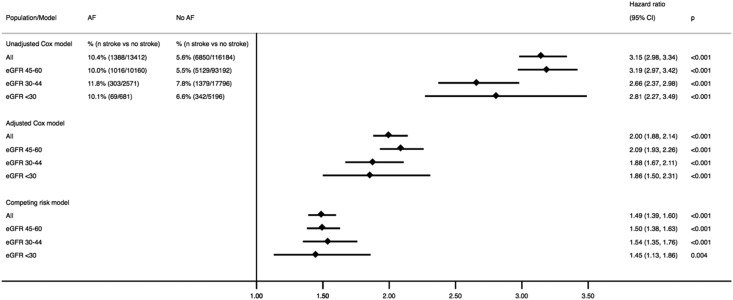
Figure 1.
The risk of all-cause stroke associated with incident atrial fibrillation (AF) in adults with nondialysis-dependent CKD overall and stratified by eGFR categories. Shown are the crude and adjusted Cox models as well as a Fine and Gray competing risk model with death due to other causes as the competing event. The interaction effect of eGFR (milliliters per minute per 1.73 m2) categories and AF was not statistically significant in the three models (P>0.10). The hazard ratio (HR) was adjusted for age, sex, eGFR (milliliters per minute per 1.73 m2), history of intracranial bleeding, history of heart failure, anemia, hypertension, diabetes, vascular disease, prior history of stroke, percutaneous coronary intervention, coronary artery bypass grafting, peripheral arterial disease, pulmonary embolism, deep venous thrombosis, valvular disease, liver disease, thyroid disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer, alcohol abuse, and dementia as well as use of warfarin, aspirin, clopidogrel, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and proton pump inhibitors. 95% CI, 95% confidence interval.