Figure 5.
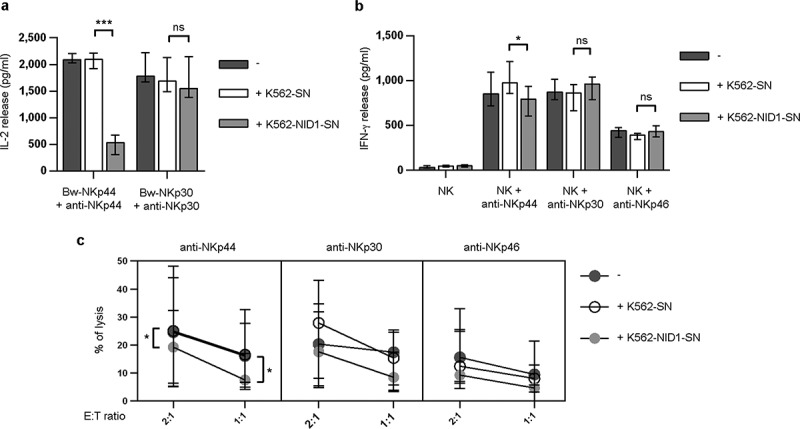
Effects of soluble NID1 on NKp44-induced function in Bw-NKp44 cells and human polyclonal NK cells. (A) Bw-NKp44 and Bw-NKp30 cells were incubated on anti-NKp44 or anti-NKp30 mAb-coated plates, respectively, for 20 h at 37°C in the absence or in the presence of SN derived from untransfected or NID1-transfected K562 cells. IL-2 release in the SN was evaluated by ELISA. The background (from GAM-stimulated cells) was subtracted for each value. Data are medians of duplicates ± interquartile range and are the pooled results of four independent experiments. ***p = 0.0002, ns = 0.1044, by two-tailed Mann Whitney test. (B) Polyclonal NK cell lines were incubated with SN derived from wild type or NID1-transfected K562 cells and cultured for 20 h at 37°C on plates coated with anti-NKp44, -NKp30, or -NKp46 mAbs. IFN-γ release in the SN was evaluated by ELISA. Data are medians of six independent experiments ± interquartile range performed with NK cells from three donors. *p = 0.0156, ns = 0.1094 (NK + anti-NKp30) and 0.0983 (NK + anti-NKp46) by one-tailed Wilcoxon test. (C) Polyclonal NK cell lines were incubated with medium or with SN derived from wild type or NID1-transfected K562 cells. After 20 h cells were utilized in a redirected killing assay against the FcγR+ P815 target cell line in the absence or in the presence of the indicated mAbs (E:T ratios 2:1 and 1:1). Data are medians of duplicates ± interquartile range and are the pooled results of six experiments performed with NK cells derived from three donors *p = 0.0313 (2:1 ratio) and 0.0156 (1:1 ratio) by one-tailed Wilcoxon test.
